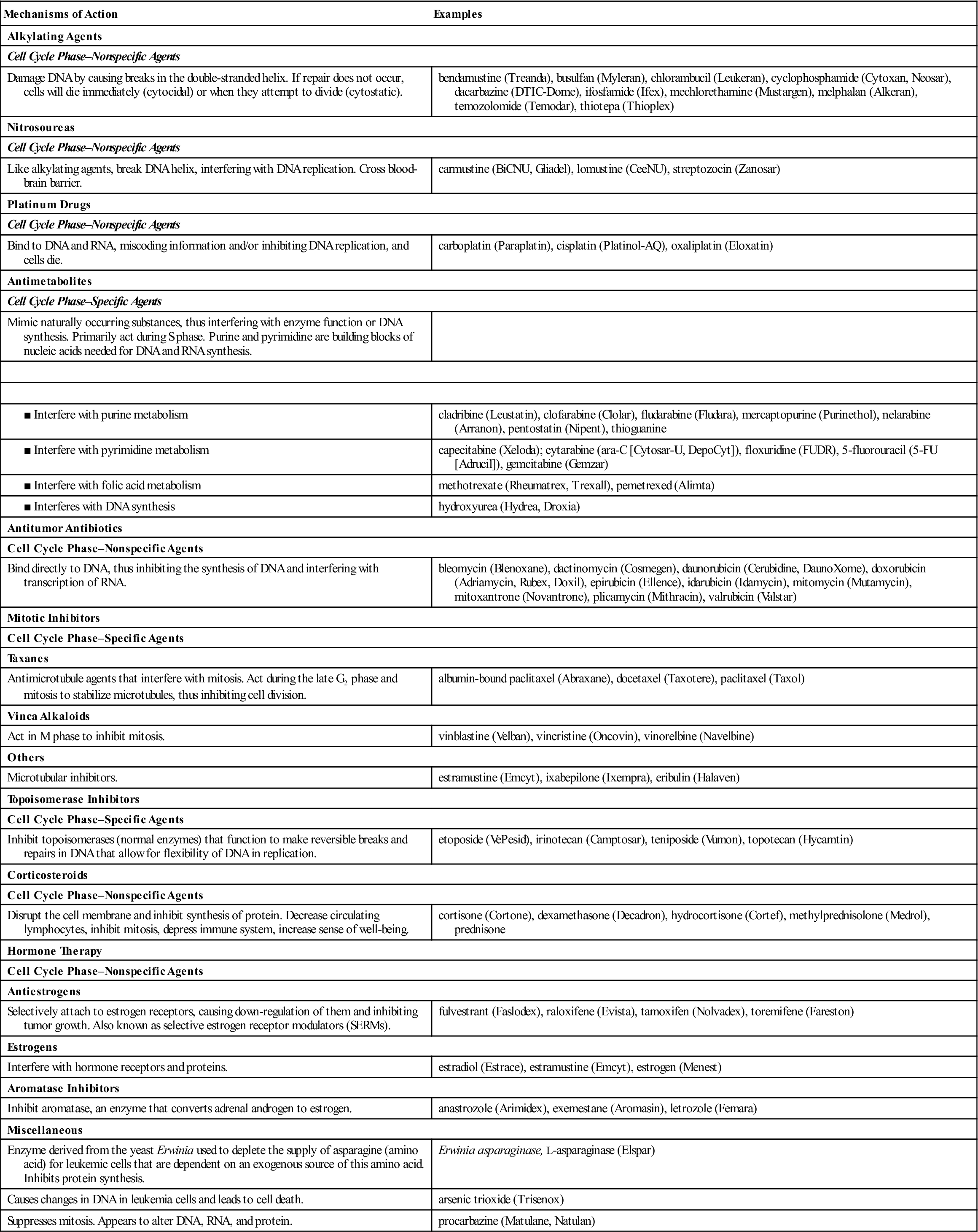
Alkylating Agents |
Cell Cycle Phase–Nonspecific Agents |
Damage DNA by causing breaks in the double-stranded helix. If repair does not occur, cells will die immediately (cytocidal) or when they attempt to divide (cytostatic). |
bendamustine (Treanda), busulfan (Myleran), chlorambucil (Leukeran), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan, Neosar), dacarbazine (DTIC-Dome), ifosfamide (Ifex), mechlorethamine (Mustargen), melphalan (Alkeran), temozolomide (Temodar), thiotepa (Thioplex) |
Nitrosoureas |
Cell Cycle Phase–Nonspecific Agents |
Like alkylating agents, break DNA helix, interfering with DNA replication. Cross blood-brain barrier. |
carmustine (BiCNU, Gliadel), lomustine (CeeNU), streptozocin (Zanosar) |
Platinum Drugs |
Cell Cycle Phase–Nonspecific Agents |
Bind to DNA and RNA, miscoding information and/or inhibiting DNA replication, and cells die. |
carboplatin (Paraplatin), cisplatin (Platinol-AQ), oxaliplatin (Eloxatin) |
Antimetabolites |
Cell Cycle Phase–Specific Agents |
Mimic naturally occurring substances, thus interfering with enzyme function or DNA synthesis. Primarily act during S phase. Purine and pyrimidine are building blocks of nucleic acids needed for DNA and RNA synthesis. |
|
|
cladribine (Leustatin), clofarabine (Clolar), fludarabine (Fludara), mercaptopurine (Purinethol), nelarabine (Arranon), pentostatin (Nipent), thioguanine |
|
capecitabine (Xeloda); cytarabine (ara-C [Cytosar-U, DepoCyt]), floxuridine (FUDR), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU [Adrucil]), gemcitabine (Gemzar) |
|
methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexall), pemetrexed (Alimta) |
|
hydroxyurea (Hydrea, Droxia) |
Antitumor Antibiotics |
Cell Cycle Phase–Nonspecific Agents |
Bind directly to DNA, thus inhibiting the synthesis of DNA and interfering with transcription of RNA. |
bleomycin (Blenoxane), dactinomycin (Cosmegen), daunorubicin (Cerubidine, DaunoXome), doxorubicin (Adriamycin, Rubex, Doxil), epirubicin (Ellence), idarubicin (Idamycin), mitomycin (Mutamycin), mitoxantrone (Novantrone), plicamycin (Mithracin), valrubicin (Valstar) |
Mitotic Inhibitors |
Cell Cycle Phase–Specific Agents |
Taxanes |
Antimicrotubule agents that interfere with mitosis. Act during the late G2 phase and mitosis to stabilize microtubules, thus inhibiting cell division. |
albumin-bound paclitaxel (Abraxane), docetaxel (Taxotere), paclitaxel (Taxol) |
Vinca Alkaloids |
Act in M phase to inhibit mitosis. |
vinblastine (Velban), vincristine (Oncovin), vinorelbine (Navelbine) |
Others |
Microtubular inhibitors. |
estramustine (Emcyt), ixabepilone (Ixempra), eribulin (Halaven) |
Topoisomerase Inhibitors |
Cell Cycle Phase–Specific Agents |
Inhibit topoisomerases (normal enzymes) that function to make reversible breaks and repairs in DNA that allow for flexibility of DNA in replication. |
etoposide (VePesid), irinotecan (Camptosar), teniposide (Vumon), topotecan (Hycamtin) |
Corticosteroids |
Cell Cycle Phase–Nonspecific Agents |
Disrupt the cell membrane and inhibit synthesis of protein. Decrease circulating lymphocytes, inhibit mitosis, depress immune system, increase sense of well-being. |
cortisone (Cortone), dexamethasone (Decadron), hydrocortisone (Cortef), methylprednisolone (Medrol), prednisone |
Hormone Therapy |
Cell Cycle Phase–Nonspecific Agents |
Antiestrogens |
Selectively attach to estrogen receptors, causing down-regulation of them and inhibiting tumor growth. Also known as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). |
fulvestrant (Faslodex), raloxifene (Evista), tamoxifen (Nolvadex), toremifene (Fareston) |
Estrogens |
Interfere with hormone receptors and proteins. |
estradiol (Estrace), estramustine (Emcyt), estrogen (Menest) |
Aromatase Inhibitors |
Inhibit aromatase, an enzyme that converts adrenal androgen to estrogen. |
anastrozole (Arimidex), exemestane (Aromasin), letrozole (Femara) |
Miscellaneous |
Enzyme derived from the yeast Erwinia used to deplete the supply of asparagine (amino acid) for leukemic cells that are dependent on an exogenous source of this amino acid. Inhibits protein synthesis. |
Erwinia asparaginase, L-asparaginase (Elspar) |
Causes changes in DNA in leukemia cells and leads to cell death. |
arsenic trioxide (Trisenox) |
Suppresses mitosis. Appears to alter DNA, RNA, and protein. |
procarbazine (Matulane, Natulan) |