Do not confuse cabazitaxel with paclitaxel or Paxil, or Jevtana with Januvia, Levitra, or Sentra. (Apo-Calcitonin Do not confuse calcitonin with calcitriol, or Miacalcin with Micatin. Do not confuse Citracal with Citrucel, OsCal with Asacol, or PhosLo with ProSom. Calcium Chloride • May give undiluted or may dilute with 0.9% NaCl or Sterile Water for Injection. Calcium Gluconate • May give undiluted or may dilute with 100 ml 0.9% NaCl or D5W. Storage • Store at room temperature. • Once diluted, stable for 24 hrs at room temperature. BLACK BOX ALERT May increase anticoagulant effect of warfarin. Do not confuse Xeloda with Xenical.
C
cabazitaxel
calcitonin
![]() , Calcimar
, Calcimar ![]() , Caltine
, Caltine ![]() , Fortical, Miacalcin)
, Fortical, Miacalcin)
calcium gluconate
Administration/handling
![]() IV
IV
capecitabine
![]()
![]()
C
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification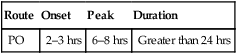
 classification
classification classification
classification

