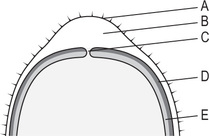
cabbage leaves traditional herbal remedy for breast engorgement or oedema; green or white cabbage leaves are wiped clean, cooled in refrigerator, applied to breasts or legs, allowing excess fluid to exude by osmosis; leaves are left until wet then replaced, process being repeated until relief is obtained. Leaves should not be washed or frozen as this will trigger osmosis, negating therapeutic effects.
cabergoline dopamine receptor agonist, drug for anovulatory hyperprolactinaemia with less side effects than bromocryptine.
caecum blind pouch, e.g. proximal part of large intestine, from which extends vermiform appendix.
Caesarean section obstetric operation to extract fetus from uterus through incision in abdominal and uterine walls after 24 weeks of pregnancy. Classical C. s. involves vertical incision in uterine body, scar is more likely to rupture in subsequent pregnancies. Crash C. s. immediate surgery required during labour for cord prolapse, uterine rupture, antepartum haemorrhage. Elective C. s. planned antenatally, for true cephalopelvic disproportion; major placenta praevia, high-order multiple pregnancy, serious maternal medical or obstetric conditions. Emergency C. s. performed when complications occur in labour, e.g. fetal distress; failure to progress, malpresentation or malposition preterm delivery when extrauterine environment is safer than intrauterine environment. Lower segment C. s. (LSCS) involves horizontal incision in lower uterine segment to reduce risks of uterine rupture during subsequent labour. Vaginal birth after C. s. (VBAC) trial labour may be offered for women with previous C. s. scar on uterus, to enable them to attempt vaginal birth.
calcaneum, calcaneus bone of foot forming heel.
calcification deposit of lime in tissue, sometimes found in mature or postmature placenta.
calcium chemical element; in combination with phosphorus, forms calcium phosphate of bones and teeth. Ca ion positively charged ion in intra- and extracellular fluid, essential for blood clotting, maintenance of normal heart beat, initiation of neuromuscular and metabolic activities; vitamin D is essential for absorption. Pregnant women should eat calcium-containing foods, e.g. cheese, yogurt, milk, green vegetables, or supplements may be given. Tetany from hypocalcaemia may occur in newborn babies. Symbol Ca. C. channel blockers drugs which block calcium entry into cardiac and arterial muscle cells to decrease contraction of heart and dilate arteries, causing vasodilatation and reducing arterial pressure. Nifedipine is increasingly used as antihypertensive drug in pregnancy and can be given in rapid-release formula to reduce blood pressure quickly in acute situations. May cause serious hypotension if used in combination with magnesium sulphate. Side effects include headache; differentiation between side effect and onset of fulminating pre-eclampsia is essential.
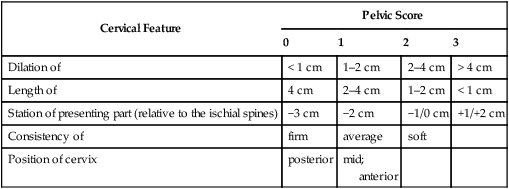
Cervical Feature |
Pelvic Score |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
Dilation of |
< 1 cm |
1–2 cm |
2–4 cm |
> 4 cm |
Length of |
4 cm |
2–4 cm |
1–2 cm |
< 1 cm |
Station of presenting part (relative to the ischial spines) |
−3 cm |
−2 cm |
−1/0 cm |
+1/+2 cm |
Consistency of |
firm |
average |
soft |
|
Position of cervix |
posterior |
mid;
anterior |
|
|
calculus stone formed in gallbladder, bile duct, kidney or ureter. Pl calculi.
Calder score modified bishop’s score, method of assessing ease with which mother will commence labour after induction.
Caldicott guardian named member of NHS Trust responsible for agreeing and reviewing internal protocols governing protection and use of patientidentified information by staff within healthcare system.
calendar calculation assessment of female menstrual cycle, calculated according to length of cycles in previous 6–12 months used as a method of natural family planning.
calipers compasses for measuring diameters and curved surfaces, e.g. fetal skull.
callus 1. tissue that grows around fractured ends of bone and develops into new bone to repair injury. 2. localised hyperplasia of horny layer of epidermis caused by pressure or friction.
calorie unit of heat, amount needed to raise temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C. Used to measure body heat and energy needs in food. Pregnant or breastfeeding mothers need about 2500 kcal/day; full-term infant needs 110 kcal/kg body weight/day after fourth day of life. SI counterpart is joule (J), equal to 4.2 cal.
cancer See carcinoma.
Candida albicans yeast-like fungus, part of normal flora of mouth, skin, intestinal tract and vagina, but may also cause infections. See also candidiasis. C. albicans pathogen causing ‘thrush’ infection.
candidiasis mucous membrane infected with Candida albicans, particularly affecting vagina, skin, mouth or nails; may also invade bronchi and lungs; can become systemic.
Canesten See clotrimazole.
cannula tube for insertion into cavity or blood vessel; trocar used to aid insertion.
capillary hair-like, minute vessels connecting arterioles and venules, with semipermeable walls to facilitate interchange of substances between blood and tissue fluid; also occur in lymphatic system. C. haemangiomata ‘strawberry marks’, red raised skin lesions appearing in first weeks of life, more common in girls and preterm infants; treatment rarely required, usually disappears by age 5–6.
caput head. C. succedaneum oedematous swelling of fetal head, present at birth, due to pressure from dilating cervical os, which, after forewater rupture restricts venous return in superficial tissues; pits on pressure, can cross suture lines on scalp; may occur on face in face presentation; bruising may also occur; usually disperses within hours. See also cephalhaematoma.
carbamazepine anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug used primarily for epilepsy and bipolar disorder; considered relatively safe in pregnancy.
carbimazole drug to treat thyrotoxicosis; use in pregnancy may cause fetal hypothyroidism.
carbohydrate food composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO); sugar, starch, cellulose foods that provide heat and energy; may be stored as glycogen for future use or, in excessive amounts, as fats.
carbon dioxide (CO2) gas present in minute quantities in atmosphere; formed in body tissues by carbon oxidation and excreted by lungs; used with oxygen to stimulate respiration; usually measured as PaCO2.
carbon monoxide (CO) colourless, odourless, tasteless gas, formed by burning carbon or organic fuels with minimal oxygen; inhalation causes central nervous system damage and asphyxiation.
carbonate carbonic acid salt.
carboprost synthetic prostaglandin analogue of PGF2α with oxytocic properties; used in postpartum haemorrhage caused by atonic uterus not controlled by other methods. Contraindication: cardiovascular, renal and hepatic disease and pelvic inflammatory disease; precautions: asthma, anaemia, jaundice, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, previous Caesarean section or other uterine surgery. Side effects: sudden onset diarrhoea, nausea.
carcinogenic causing carcinoma.
carcinoma malignant epithelial tumour; cancer.
cardia 1. cardiac opening. 2. cardiac part of stomach surrounding oesophagogastric junction, distinguished by presence of cardiac glands.
cardiac pertaining to heart. C. anomalies congenital defects, including transposition of great vessels, pulmonary or tricuspid atresia, tetralogy of fallot, total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage, univentricular or complex heart structure. C. arrest sudden, often unexpected cessation of heart action requiring emergency cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). See appendix 2 AND 3. C. disease in pregnancy most commonly results from congenital heart disease. In pregnancy, often worsens due to increased stress on heart; careful monitoring is essential; long-term hospital admission may be necessary. Labour care aims to prevent problems of overexertion and cardiac overload although first stage is often short; forceps delivery or Caesarean may avoid need for active second-stage pushing; third stage is most dangerous due to increased blood volume from strong uterine contractions, may be exacerbated by oxytocics. C. output increased in pregnancy due to increased stroke volume and heart rate, especially first trimester; may be affected by supine hypotensive syndrome.
cardinal ligaments transverse cervical or Mackenrodt’s ligaments; two thickened bands of parametrium stretching from uterine cervix to lateral walls of pelvis; help to support uterus.
cardiogenic shock impaired ability of heart to pump blood, sometimes seen after pulmonary embolism or in mother with cardiac defects.
cardiogram graphic representation of heart’s action traced by electrocardiograph.
cardiomegaly enlarged heart involving inflammation and enlargement of myocardium.
cardiomyopathy, postpartum rare complication of late pregnancy and peripartum period, with 25% to 50% mortality; cardiomyopathy causes left ventricular heart failure and thromboembolic problems; associated with older, multiparous women, obesity, hypertension, diabetes. Management focuses on relieving congestive heart failure symptoms; occasionally, heart transplant is necessary.
cardiotocography (CTG) fetal heart activity (cardio-) and uterine contraction (-toco-) recording (-graphy) to assess fetal well-being in pregnancy or labour, via transducers on maternal abdomen; fetal heart rate may be assessed via fetal scalp electrode during labour once membranes are ruptured. Recording is analysed for reduced baseline variability, decelerations and irregularities in fetal heart rate in response to maternal uterine action, aids detection of fetal hypoxia.
cardiovascular relating to heart and blood vessels.
caries decay or necrosis of bone. Dental c. decay of teeth.
carneous mole blood mole, fleshy mole, missed abortion; mass of blood clots surrounding dead embryo, retained by uterus. See tubal mole.
carotene deep yellow pigment converted to vitamin A by liver; found in yellow and orange fruit, vegetables.
carotid bodies small neurovascular structures in bifurcation of right and left carotid arteries containing chemoreceptors that monitor oxygen content in blood and help to regulate respiration.
carpal tunnel syndrome hand tingling and numbness resulting from pressure on median nerve within carpal tunnel in wrist. In pregnancy, local oedema increases pressure; often worse at night, may be relieved by sleeping with hands splinted. More severe cases may need physiotherapy, or osteopathy; usually resolves spontaneously after delivery although occasionally surgery is required.
carpopedal spasm muscular spasm of hands and feet in tetany.
carrier 1. person who carries pathogenic organisms in body without symptoms of disease; organisms may be passed to others. 2. in genetics, an apparently normal individual who carries recessive or sex-linked gene. C. oil oil, e.g. grapeseed, in which essential oils used in aromatherapy are diluted and applied to skin in massage.
cartilage fibrous connective tissue in adults, forming most of temporary skeleton in embryo, providing model in which most of bones develop and constituting important part of organism’s growth mechanism.
carunculae myrtiformes small elevations of mucous membrane around vaginal orifice; remnants of ruptured hymen.
cascade of intervention iatrogenic consequences of intervening in normal physiological process of labour, including untimely attempts to induce labour, artificially rupturing membranes before or during labour, effects of medications for pain relief, dorsal position, etc, which interfere with adequate oxytocin release, adversely affect woman’s ability to push baby out, increase infection risk.
case conference meeting of professionals involved in care of particular person (often child), to agree patterns of action and monitor progress.
casein one of proteins of milk; less digestible and present in larger quantities in cows’ milk than in human milk. C. dominant infant formula milk formulae with same proportion of macronutrients as whey dominant formulae, but greater amount of protein is casein; aimed at babies with greater appetite as relatively indigestible curds derived from casein make baby feel fuller longer, increasing metabolic demands.
caseinogen precursor of casein; converted into casein by rennin in gastric juice of babies.
caseload midwifery midwifery care system; each midwife is responsible for group of women, i.e. caseload, aimed at improving communication and continuity of care.
case mix database computerised record system combining all data received from patient administration and operational systems to provide comprehensive information about treatments and services received during episodes of care.
caspofungin antifungal drug, effective against Candida and Aspergillus; administered intravenously.
cast structure moulded in hollow organ, retaining shape of cavity of organ when shed, e.g. decidual cast shed from uterus in tubal pregnancy, casts from renal tubules in urine in kidney disease.
castor oil oil sometimes ingested by women keen to avoid medical labour induction for post-dates pregnancy; causes severe diarrhoea with possible dehydration, but generally ineffective for inducing contractions.
castration removal of male testicles or female ovaries.
catamenia menstruation.
cataract opacity of crystalline lens or its capsule, which impairs vision. Congenital c. sometimes occurs due to familial condition or maternal rubella in early pregnancy; associated with galactosaemia.
catecholamine sympathomimetic amines (dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine), involved in physiological stress response. Release at sympathetic nerve endings increases cardiac output and constricts peripheral blood vessels, increasing blood pressure; blood glucose is increased through hepatic and skeletal muscle glycogenesis; blood lipids raised by increasing fat catabolism.
catgut suture material made from sheep gut, absorbed by body; used mainly for buried sutures.
catheter polythene, rubber, gum elastic or silver tube, perforated near its blind end; introduced into various hollow organs, vessels or canals for catheterisation.
catheterisation insertion of catheter to introduce or withdraw fluid or to measure fluid pressure, e.g. bladder, umbilicus.
cathode negative electrode.
cation ion carrying positive electric charge, e.g. sodium, copper.
cauda equina nerves into which spinal cord divides at its termination in lumbar region.
caudal block regional analgesia; introduction of drugs through sacral hiatus; less reliable than entering epidural space by lumbar route. See epidural analgesia.
caul rare condition; amnion fails to rupture in labour, enveloping baby’s head at birth; should be ruptured quickly to establish clear airway.
caulophyllum homeopathic remedy sometimes appropriate to induce or accelerate labour, but not suitable for all women; inappropriate use may cause hypertonic uterine action or, more commonly, prostin-like contractions which are intense, painful but ineffective in encouraging cervical dilatation. Midwives must be appropriately trained to use homeopathy.
cautery hot instrument or chemical agent used to destroy tissue by burning it, e.g. cervical erosion.
cavity of pelvis hollow within pelvic walls, bounded by pelvic brim (inlet) above and outlet below.
-cele suffix meaning ‘tumour’, e.g. meningocele.
cell structural unit of all multicellular organisms, consisting of nucleus with central nucleolus, chromosomes with surrounding semifluid cytoplasm containing mitochondria, ribosomes, other bodies, within cell membrane. All living cells arise from other cells, either by division of one cell to make two, as in mitosis and meiosis, or by fusion of two cells to make one, e.g. fusion of sperm and ovum to make zygote. Cells differentiate during development into specialised types organised into tissues, then into organs.
cellulitis diffuse inflammatory process within solid tissues, characterised by oedema, redness, pain, functional disturbance, caused by infection with streptococci, staphylococci etc. Occurs in loose tissues beneath skin or, less commonly, mucous membranes, or around muscle bundles or surrounding organs. See also parametritis.
cellulose carbohydrate; fibrous outer covering of vegetable cells, indigestible in human alimentary tract but gives bulk and stimulates peristalsis.
Celsius internationally recognised unit of temperature (°C), water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
census enumeration of population, introduced in England and Wales in 1801, repeated every 10 years; records name, address, sex, occupation, marital status, other social information of every household.
centile See percentile.
centimetre one-hundredth of metre.
central nervous system brain and spinal cord.
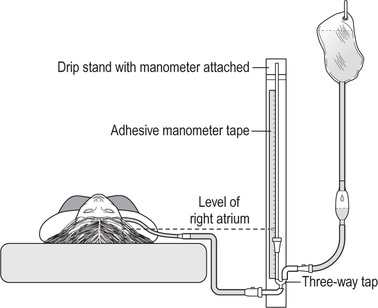
central venous pressure (CVP) pressure of blood in right atrium; indicating balance between cardiac output and venous return, measured via catheter inserted through median cubital vein to superior vena cava; distal end of catheter is attached to manometer, positioned at bedside so that zero point is at level of right atrium; each time mother’s position is changed, zero point on manometer must be reset. Used to assess accurately amount of blood lost during haemorrhage, e.g. in concealed placental abruption, and to ensure adequate fluid replacement without overloading circulation. Normal fluid volume range in right atrium is 15 to 110 cm of saline when zero point of scale corresponds to midaxillary line.
centrifuge apparatus to rotate test tubes at great speed to precipitate bacteria, cells and other substances.
cephalhaematoma collection of blood beneath periosteum of one cranial bone, causes fluctuant swelling to develop on baby’s head within 48 hours of birth;. distinguished from caput succedaneum as develops after birth and is limited to one bone; takes several weeks to subside; no treatment necessary unless severe jaundice occurs.
cephalic pertaining to head, usually fetal head. C. presentation normal presentation of fetus, i.e. with head in lowest pole of uterus. C. version conversion to head presentation. See version.
cephalometry head measurement, used antenatally to measure biparietal diameter to assess fetal maturity and growth, most accurately by ultrasound.
cephalopelvic relationship of fetal head to maternal pelvis. C. disproportion misfit between fetal head and maternal pelvis, assumed when fetal head will not engage in pelvis
after 36 weeks’ gestation; may be diagnosed in labour; may cause obstructed labour.
cephaloridine antibiotic derived from cephalosporin; if given antenatally orally, intramuscularly or intravenously crosses placenta, entering fetal circulation.
cephalosporin naturally occurring antibiotic, chemically similar to penicillin.
cerclage encircling with ring or loop of non-absorbable suture, to keep cervix closed in case of incompetent cervix which causes repeated miscarriages.
cerebellum hindbrain, below cerebrum and behind medulla oblongata.
cerebral pertaining to cerebral hemispheres. C. dysrhythmia brain shows abnormal pattern of electrical waves on electroencephalograph (EEG) tracing, occurs in epilepsy and eclamptic convulsions. C. haemorrhage bleeding from or into one of cerebral hemispheres. C. palsy persistent motor disorder resulting from hypoxia in utero, asphyxia neonatorum and periods of apnoea and cyanosis, as in respiratory distress syndrome, hypoglycaemia and other conditions.
cerebrospinal relating to brain and spinal cord. C. fluid fluid in ventricles of brain, secreted by choroid plexuses, circulating in subarachnoid space and membranes surrounding spinal cord; protects nerves in brain and spinal cord from jarring and injury. Excess cerebral fluid is found in hydrocephalus.
cerebrum centre of higher functions of brain, occupying greater portion of cranium and consisting of right and left cerebral hemispheres.
cervical pertaining to neck. 1. in obstetrics, pertaining to uterine cervix. C. canal channel starting at internal cervical os, communicating with body of uterus, ending at external os, opening into vagina. C. cerclage See cerclage. C. cytology examination of cervical cells to detect abnormal changes. C. ectropion (eversion) physiological response by cervical cells to hormonal changes in pregnancy; cells proliferate, causing cervix to appear eroded. C. effacement See effacement. C. dilatation opening of cervix during first-stage labour, from tightly closed cervical os to opening large enough to allow passage of fetal head; assessed on examination per vaginam, full dilatation being approximately 10 cm. C. incompetence failure of cervix to hold pregnancy in uterus; cause of second-trimester abortion, characterised by premature membrane rupture and painless expulsion of fetus; can be treated by cervical cerclage. C. intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) classification of types of cervical dysplasia. CIN I – mild, reversible dysplasia; CIN II – moderate, reversible dysplasia; CIN III – severe, irreversible dysplasia and carcinoma in situ, requiring surgery to prevent development of invasive carcinoma. C. polyps small vascular pedunculated growths of squamous or columnar epithelium covering core of connective tissue and blood vessels, in cervical canal or ectocervix; may be asymptomatic or cause antenatal bleeding; no treatment necessary in pregnancy unless bleeding is severe or malignancy is suspected C. ripening physiological or artificially induced process by which cervix softens and becomes more susceptible to effects of uterine contractions, See bishop’s score and calder score 2. C. vertebrae small, joined neck bones.
cervicitis infection of mucous membrane lining uterine cervix. Acute c. occurs in gonorrhoea. Chronic c. usually caused by low-grade infection following tearing of cervix during delivery; inflamed mucous membrane protrudes through external os to vaginal part of cervix forming erosion, which bleeds readily; treatment by cauterisation destroys infected tissues.
cervix constricted portion or neck. C. uteri neck of uterus opening into vagina; 2.5 cm long.
Chadwick’s sign dark purplish discoloration and congestion of vaginal membrane caused by increased vascularity; sign of pregnancy but occurs in any condition with pelvic congestion.
chancre initial lesion of syphilis, developing at site of inoculation.
charge syndrome genetic condition including defects of eyes, heart and ears, oesophageal atresia and growth retardation; may be associated with choanal atresia; leading cause of congenital deafness and blindness.
chemical change profound alteration in chemical properties, usually permanent, and accompanied by use of energy in new substance, e.g. hydrogen plus oxygen produces water.
chemical compound substance produced by chemical change, can be broken up into its components only by chemical means, unlike a mixture, which can be separated mechanically.
chemoreceptor collection of cells sensitive to alterations in chemicals contacting them, found in carotid and aortic body; responsive to changes in oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion concentration in blood. When oxygen concentration falls below normal in arterial blood, chemoreceptors send impulses to stimulate respiratory centre to increase alveolar ventilation and consequently oxygen intake by lungs.
chemotherapy treatment of illness by chemical means, i.e. with medication. Adj chemotherapeutic.
chest
Only gold members can continue reading.
Log In or
Register to continue
Related
![]()