Describe any breast mass or lump that you encounter using the following characteristics: • Location: clock positions and distance from nipple • Size (in centimeters): length, width, thickness • Shape: round, discoid, lobular, stellate, regular or irregular • Consistency: firm, soft, hard • Mobility: movable (in what directions) or fixed to overlying skin or subadjacent fascia • Borders: discrete or poorly defined • Retraction: presence or absence of dimpling; altered contour All new solitary or dominant masses must be investigated with further diagnostic testing. Axillary: Support patient’s forearm with your contralateral arm and bring palm of examining hand flat into axilla. With palmar surface of fingers, reach deep into hollow, pushing firmly upward, then bring fingers down, rotating your fingers and gently rolling soft tissue against chest wall and axilla. Explore apex, medial, lateral aspects along rib cage; lateral aspects along upper surface of arm; and anterior and posterior walls of axilla. Repeat mirror image of this maneuver for the other axilla. Supraclavicular area: Hook fingers over clavicle and rotate over supraclavicular fossa while patient turns head toward same side and raises shoulder. Infraclavicular area: Palpate along the clavicle using a rotary motion with your fingers.
Breasts and Axillae
Examination
Technique
Findings
Female Patients
With patient seated and arms hanging loosely, inspect both breasts
Inspect all quadrants and tail of Spence. If necessary, lift breasts with fingertips to expose lower and lateral aspects.
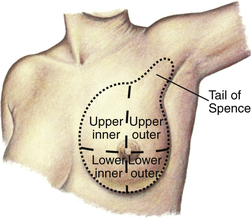
EXPECTED: Convex, pendulous, or conical. Frequently asymmetric in size.
EXPECTED: Smooth and uninterrupted.
UNEXPECTED: Dimpling or peau d’orange appearance. Changes or asymmetric appearance.
EXPECTED: Consistent color
UNEXPECTED: Areas of discoloration, erythema, or asymmetric appearance.
EXPECTED: Bilateral venous networks, although usually pronounced only in pregnant women.
UNEXPECTED: Unilateral network.
EXPECTED: Long-standing nevi. Supernumerary nipples possible (but could be a clue to other congenital abnormalities).
UNEXPECTED: Changing or tender nevi. Lesions.
Inspect areolae and nipples
EXPECTED: Areolae round or oval, bilaterally equal or nearly equal. Nipples bilaterally equal or nearly equal in size and usually everted, although one or both sometimes inverted.
UNEXPECTED: Recent unilateral nipple inversion or retraction.
EXPECTED: Areolae and nipples pink to brown.
UNEXPECTED: Nonhomogeneous in color.
EXPECTED: Areolae smooth, except for Montgomery tubercles. Nipples smooth or wrinkled.
UNEXPECTED: Areolae with suppurative or tender Montgomery tubercles or with peau d’orange appearance. Nipples crusting, cracking, or with discharge.
With patient in the following positions, reinspect both breasts
EXPECTED: All positions breasts bilaterally symmetric with even contour.
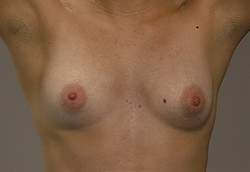
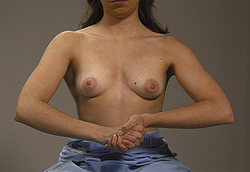
UNEXPECTED: Dimpling, retraction, deviation, or fixation of breasts. 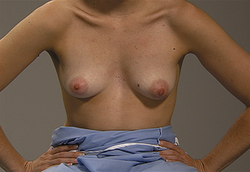
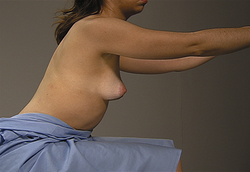
With patient seated and arms hanging loosely, palpate breasts
Chest wall sweep. Place the palm of your right hand at the patient’s right clavicle at the sternum. Sweep downward from the clavicle to the nipple, feeling for superficial lumps. Repeat the sweep until you have covered the entire right chest wall. Repeat the procedure using your left hand for the left chest wall. 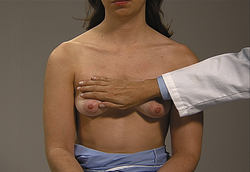
EXPECTED: Tissue smooth, free of lumps.
UNEXPECTED: Lumps or nodules. Reassess with additional palpation and characterize any masses by location, size, shape, consistency, tenderness, mobility, delineation of borders, retraction. Use transillumination to assess presence of fluid in masses.
Bimanual digital palpation. Place one hand, palmar surface facing up, under the patient’s right breast. Position your hand so that it acts as a flat surface against which to compress the breast tissue. Walk the fingers of the other hand across the breast tissue, feeling for lumps as you compress the tissue between your fingers and your flat hand. Repeat the procedure for the other breast. 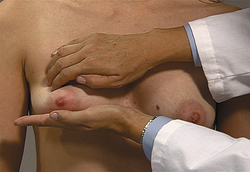
EXPECTED: Tissue generally firm, nontender, free of lumps. During menstrual cycle, cyclic pattern of breast enlargement, increased nodularity, tenderness.
UNEXPECTED: Lumps or nodules. Reassess with additional palpation and characterize any masses by location, size, shape, consistency, tenderness, mobility, delineation of borders, retraction. Use transillumination to assess presence of fluid in masses.
With patient seated, palpate for lymph nodes
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

Breasts and Axillae
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access