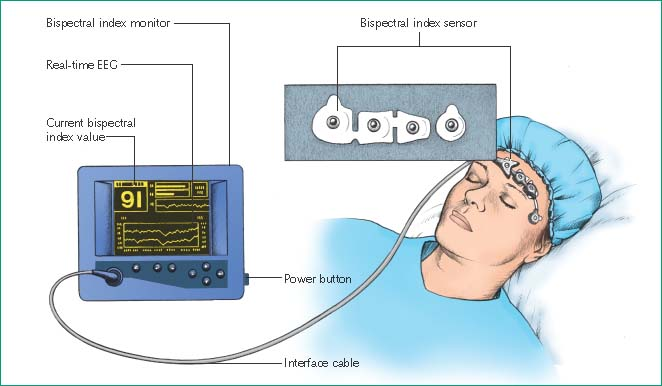
Bispectral Index Monitoring
Bispectral index monitoring involves the use of an electronic device that converts EEG waves into a number. This number, statistically derived from raw EEG data, indicates the depth or level of a patient’s sedation and provides a direct measure of the effects of sedatives and anesthetics on the brain. Rather than relying on subjective assessments and vital signs, bispectral index monitoring
provides objective, reliable data on which to base care, thus minimizing the risks of oversedation and undersedation. When used appropriately, bispectral index monitoring can decrease the total amount of sedation needed to keep a patient adequately sedated.
provides objective, reliable data on which to base care, thus minimizing the risks of oversedation and undersedation. When used appropriately, bispectral index monitoring can decrease the total amount of sedation needed to keep a patient adequately sedated.
The bispectral index monitor is attached to a sensor applied to the patient’s forehead. The sensor obtains information about the patient’s electrical brain activity and then translates this information into a number from 0 (indicating no brain activity) to 100 (indicating a patient who’s awake and alert). In the critical care unit, bispectral index monitoring is used to assess sedation when the patient is receiving mechanical ventilation or neuromuscular blockers or during barbiturate coma or bedside procedures.
Equipment
Bispectral index monitor and cable ▪ bispectral index sensor ▪ alcohol pads ▪ gauze pad ▪ soap and water.
Implementation
Gather the necessary equipment.
Place the bispectral index monitor close to the patient’s bed, and plug the power cord into the wall outlet.
Turn on the monitor to allow it to initiate a self-test to make sure the equipment is functioning properly.
Confirm the patient’s identity using at least two patient identifiers according to your facility’s policy.1
Explain the procedure and rationale to the patient and his family. (See Bispectral index monitoring.)
Provide privacy.
Clean the patient’s forehead with soap and water and allow it to dry. If necessary, wipe the forehead with an alcohol pad and then dry it with a gauze pad to ensure that the skin is oil-free.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access