Chapter 35 (fer-men-TAY-shun) Chemical change that is brought about by the action of an enzyme or microorganism *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts to make the combining form. Biotechnology applies scientific and engineering techniques to the manipulation of the genes of living organisms. Biotechnology includes a broad range of improvements that may be applied to plants or animals and their products (Box 35-1). More than 111 vaccines and biologics have been approved by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) for improving the health of livestock, poultry, and companion pets. In 2009, 80% to 90% of all soybean, corn, and cotton crops in the United States were bioengineered. Most of the genetic engineering was to allow the plant to produce its own insecticide or resist herbicides used to kill weeds. Biotechnologists research medical disorders and create drugs and proteins that can affect the cell. According to the March of Dimes organization, 1 in 150 live births have a chromosomal abnormality. Biotechnologists also directly alter or change the cells of living things to discover and improve genetic traits (Box 35-2). More than 200 therapies and vaccines have been created to treat cancer, diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and autoimmune disorders. Scientists have been using natural techniques of biotechnology such as fermentation, selective breeding, and artificial insemination for many years. This emerging field began to take form as a separate discipline in the early 1980s with the development of cloning and recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) techniques of gene manipulation (Box 35-3). Other personnel are filling positions to design, manufacture, and operate the equipment necessary to make these techniques possible (Table 35-1). Personnel in biotechnology must show great creativity and logical thought and must be able to work independently and as part of a team. The work takes great concentration and perseverance because the results might not be available immediately. TABLE 35-1 Biotechnology Career Educational Cost and Earnings *http://www.swu.edu/financial_aid/tuition_fees.htm.
Biotechnology Research and Development Careers
 Define at least 10 terms relating to biotechnology.
Define at least 10 terms relating to biotechnology.
 Identify the function of the biotechnological health care team.
Identify the function of the biotechnological health care team.
 Describe the role of at least five of the biotechnological health care team members, including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
Describe the role of at least five of the biotechnological health care team members, including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
 Describe the structure, function, and method of replication of DNA.
Describe the structure, function, and method of replication of DNA.
 Describe three research techniques used by biotechnologists.
Describe three research techniques used by biotechnologists.
 Describe at least three ethical concerns that have been raised since the beginning of DNA research.
Describe at least three ethical concerns that have been raised since the beginning of DNA research.
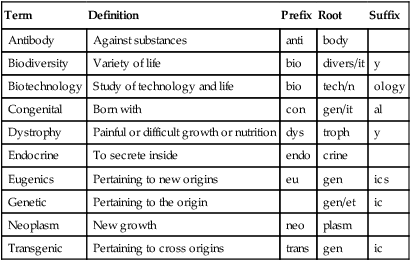
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
Antibody
Against substances
anti
body
Biodiversity
Variety of life
bio
divers/it
y
Biotechnology
Study of technology and life
bio
tech/n
ology
Congenital
Born with
con
gen/it
al
Dystrophy
Painful or difficult growth or nutrition
dys
troph
y
Endocrine
To secrete inside
endo
crine
Eugenics
Pertaining to new origins
eu
gen
ics
Genetic
Pertaining to the origin
gen/et
ic
Neoplasm
New growth
neo
plasm
Transgenic
Pertaining to cross origins
trans
gen
ic
Careers
Biotechnologist
Career
Educational Cost*
Earnings†
Forensic science technician
Southern Wesleyan University, bachelor’s degree, 82 credit hours
Fees include:
Tuition $9100/block of 12-18 hours
Fees $315/block
Books $300-$700/semester
Median annual salary: Concord, S.C.—$48,520
Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access



