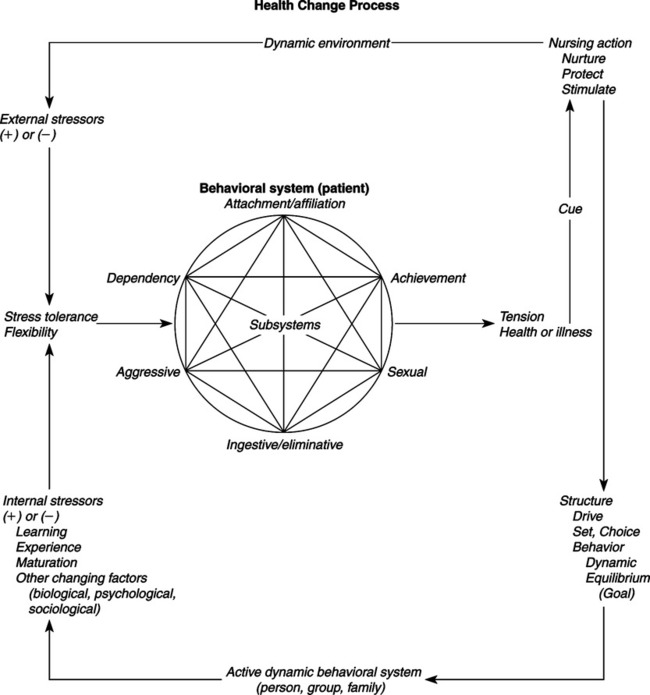
In 1955 and 1956, Johnson was a pediatric nursing advisor assigned to the Christian Medical College School of Nursing in Vellore, South India. From 1965 to 1967, she served as chairperson on the committee of the California Nurses Association that developed a position statement on specifications for the clinical specialist. Johnson’s publications include four books, more than 30 articles in periodicals, and many papers, reports, proceedings, and monographs (Johnson, 1980). Johnson’s Behavioral System Model (JBSM) was heavily influenced by Florence Nightingale’s book, Notes on Nursing (Johnson, 1992). Johnson began her work on the model with the premise that nursing was a profession that made a distinctive contribution to the welfare of society. Thus, nursing had an explicit goal of action in patient welfare. Her task was to clarify the social mission of nursing from the “perspective of a theoretically sound view of the person we serve” (Johnson, 1977). She accepted Nightingale’s belief that the first concern of nursing is with the “relationship between the person who is ill and their environment, not with the illness” (Johnson, 1977). Johnson, (1977) also noted that the “transition from this approach to the more sophisticated and theoretically sounder behavioral system orientation took only a few years and was supported by both my own, and that of many colleagues, growing knowledge about man’s action systems and by the rapidly increasing knowledge about behavioral systems.” Johnson, (1977) came to conceive of nursing’s specific contribution to patient welfare as fostering “efficient and effective behavioral functioning in the person, both to prevent illness and during and following illness.” Johnson used the work of behavioral scientists in psychology, sociology, and ethnology to develop her theory. The interdisciplinary literature that Johnson cited focused on observable behaviors that were of adaptive significance. This body of literature influenced the identification and the content of her seven subsystems. Talcott Parsons is acknowledged specifically in early developmental writings presenting concepts of the Johnson Behavioral System Model (Johnson, 1961b). Parsons’ (1951, 1964) social action theory stressed a structural-functional approach. One of his major contributions was to reconcile functionalism (the idea that every observable social behavior has a function to perform) with structuralism (the idea that social behaviors, rather than being directly functional, are expressions of deep underlying structures in social systems). Thus, structures (social systems) and all behaviors have a function in maintaining the system. The components of the structure of a social system—goal, set, choice, and behavior—are the same in Parsons’ and Johnson’s theories. Johnson also relied heavily on system theory and used concepts and definitions from Rapoport, Chin, von Bertalanffy, and Buckley (Johnson, 1980). In system theory, as in Johnson’s theory, one of the basic assumptions embraces the concept of order. Another is that a system is a set of interacting units that form a whole intended to perform some function. Johnson conceptualized the person as a behavioral system, in which the behavior of the individual as a whole is the focus. It is the focus on what the individual does and why. One of the strengths of the Johnson’s Behavioral System (JBS) Theory is the consistent integration of concepts defining behavioral systems drawn from general system theory. Some of these concepts include holism, goal seeking, interrelationship/interdependency, stability, instability, subsystems, regularity, structure, function, energy, feedback, and adaptation. Johnson noted that, although the literature indicates that others support the idea that a person is a behavioral system, and that a person’s specific response patterns form an organized and integrated whole, as far as she knew, the idea was original with her. Just as the development of knowledge of the whole biological system was preceded by knowledge of its parts, the development of knowledge of behavioral systems was focused on specific behavioral responses. Empirical literature supporting the notion of the behavioral system as a whole and its usefulness as a framework for nursing decisions in research, education, and nursing practice has accumulated since it was introduced (Benson, 1997; Bhaduri & Jain, 2004; Derdiarian, 1991; Grice, 1997; Holaday, 1981, 1982; Lachicotte & Alexander, 1990; Poster, Dee, & Randell, 1997; Turner-Henson, 1992; Wilkie, 1990; Wilmoth & Ross, 1997; Wilmoth, 2007.) Developing the Behavioral System Model from a philosophical perspective, Johnson (1980) wrote that nursing contributes by facilitating effective behavioral functioning in the patient before, during, and after illness. She used concepts from other disciplines, such as social learning, motivation, sensory stimulation, adaptation, behavioral modification, change process, tension, and stress, to expand her theory for the practice of nursing. The empirical origins of this theory begin with Johnson’s use of systems thinking (synthesis). This process concentrates on the function and behavior of the whole and is focused on an understanding and an explanation of the behavioral system. Johnson’s work on the Behavioral System Model corresponded with the “systems age.” Buckley’s (1968) seminal text was published the same year that Johnson formally presented her theory at Vanderbilt University. Concepts that Johnson identified and defined in her theory are supported in the literature. She noted that Leitch and Escolona agree that tension produces behavioral changes, and that the manifestation of tension by an individual depends on both internal and external factors (Johnson, 1980). Johnson (1959b) used the work of Selye, Grinker, Simmons, and Wolff to support the idea that specific patterns of behavior are reactions to stressors from biological, psychological, and sociological sources, respectively. Johnson (1961a) suggested a difference in her model from Selye’s conception of stress. Johnson’s concept of stress “follows rather closely Caudill’s conceptualization; that is, that stress is a process in which there is interplay between various stimuli and the defenses erected against them. Stimuli may be positive in that they are present, or negative in that something desired or required is absent” (Johnson, 1961a, pp. 7-8). Selye “conceives stress as ‘a state manifested by the specific syndrome which consists of all the nonspecifically induced changes within a biologic system’” (Johnson, 1961a, p. 8). In Conceptual Models for Nursing Practice, Johnson (1980) described seven subsystems that make up her behavioral system. To support the attachmentaffiliative subsystem, she cited the work of Ainsworth and Robson. Heathers, Gerwitz, and Rosenthal have described and explained dependency behavior, another subsystem defined by Johnson. The response systems of ingestion and elimination, as described by Walike, Mead, and Sears, are also parts of Johnson’s Behavioral System. The works of Kagan and Resnik were used to support the sexual subsystem. The aggressive-protective subsystem, which functions to protect and preserve, is supported by Lorenz and Feshbach (Feshbach, 1970; Johnson, 1980; Lorenz, 1966). According to Atkinson, Feather, and Crandell, physical, creative, mechanical, and social skills are manifested by achievement behavior, another subsystem identified by Johnson (1980). The restorative subsystem was developed by faculty and clinicians in order to include behaviors such as sleep, play, and relaxation (Grubbs, 1980). Although Johnson (personal communication, 1996) agreed that “there may be more or fewer subsystems” than were originally identified, she did not support restorative as a subsystem of the Behavioral System Model. She believed that sleep is primarily a biological force, not a motivational behavior. She suggested that many of the behaviors identified in infants during their first years of life, such as play, are actually achievement behaviors. Johnson (personal communication, 1996) stated that there was a need to examine the possibility of an eighth subsystem that addresses explorative behaviors; further investigation may delineate it as a subsystem separate from the achievement subsystem. Nursing’s goal is to maintain and restore the person’s behavioral system balance and stability or to help the person achieve a more optimum level of balance and functioning. Thus, nursing, as perceived by Johnson, is an external force that acts to preserve the organization and integration of the patient’s behavior to an optimal level by means of imposing temporary regulatory or control mechanisms or by providing resources while the patient is experiencing stress or behavioral system imbalance (Brown, 2006). An art and a science, nursing supplies external assistance both before and during system balance disturbance and therefore requires knowledge of order, disorder, and control (Herbert, 1989; Johnson, 1980). Nursing activities do not depend on medical authority, but they are complementary to medicine. Johnson (1980) viewed the person as a behavioral system with patterned, repetitive, and purposeful ways of behaving that link the person with the environment. The conception of the person is basically a motivational one. This view leans heavily on Johnson’s acceptance of ethology theories, which suggest that innate, biological factors influence the patterning and motivation of behavior. She also acknowledged that prior experience, learning, and physical and social stimuli also influence behavior. She noted that to look at a person as a behavioral system, as well as to be able to see a collection of behavioral subsystems and be knowledgeable about the physiological, psychological, and sociocultural factors operating outside them, was a prerequisite to using this model (author’s class notes, 1971). Johnson identified several assumptions that are critical to understanding the nature and operation of the person as a behavioral system. We assume that there is organization, interaction and interdependency, and integration of the parts of behavior that make up the system. An individual’s specific response patterns form an organized and integrated whole. The interrelated and interdependent parts are called subsystems. Johnson, (1977) further assumed that the behavioral system tends to achieve balance among the various forces operating within and upon it. People strive continually to maintain a behavioral system balance and steady states by more or less automatic adjustments and adaptations to the natural forces impinging upon them. Johnson also recognized that people actively seek new experiences that may temporarily disturb balance. Johnson further (1977, 1980) assumed that a behavioral system, which both requires and results in some degree of regularity and constancy in behavior, is essential to human beings. Finally, Johnson, (1977) assumed that behavioral system balance reflected adjustments and adaptations by the person that are successful in some way and to some degree. This will be true even though the observed behavior may not always match cultural norms for acceptable or health behavior. Johnson perceived health as an elusive, dynamic state influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors. Health is reflected by the organization, interaction, interdependence, and integration of the subsystems of the behavioral system (Johnson, 1980). An individual attempts to achieve a balance in this system, which will lead to functional behavior. A lack of balance in the structural or functional requirements of the subsystems leads to poor health. Thus, when evaluating “health,” one focuses on the behavioral system and system balance and stability, effective and efficient functioning, and behavioral system imbalance and instability. The outcomes of behavior system balance are as follows: (1) a minimum expenditure of energy is required (implying that more energy is available to maintain health, or, in the case of illness, that energy is available for the biological processes needed for recovery); (2) continued biological and social survival are ensured; and (3) some degree of personal satisfaction accrues (Grubbs, 1980; Johnson 1980). In Johnson’s theory, the environment consists of all the factors that are not part of the individual’s behavioral system, but that influence the system. The nurse may manipulate some aspects of the environment so that the goal of health or behavioral system balance can be achieved for the patient (Brown, 2006). The behavioral system “determines and limits the interaction between the person and their environment and establishes the relationship of the person to the objects, events and situations in the environment” (Johnson, 1978). Such behavior is orderly and predictable. It is maintained because it has been functionally efficient and effective most of the time in managing the person’s relationship to the environment. It changes when this is no longer the case, or when the person desires a more optimum level of functioning. The behavioral system has many tasks and missions to perform in maintaining its own integrity and in managing the system’s relationship to its environment. The behavioral system attempts to maintain equilibrium in response to environmental factors by adjusting and adapting to the forces that impinge on it. Excessively strong environmental forces disturb the behavioral system balance and threaten the person’s stability. An unusual amount of energy is required for the system to reestablish equilibrium in the face of continuing forces (Loveland-Cherry & Wilkerson, 1983). The environment is also the source of the sustenal imperatives of protection, nurturance, and stimulation that are necessary prerequisites to maintaining health (behavioral system balance) (Grubbs, 1980). When behavioral system imbalance (disequilibrium) occurs, the nurse may need to become the temporary regulator of the environment and provide the person’s supply of functional requirements, so the person can adapt to stressors. The type of functional requirements and the amount needed will vary by such variables as age, gender, culture coping ability, and type and severity of illness. The Johnson Behavioral System Theory addresses the metaparadigm concepts of person, environment, and nursing. The person is a behavioral system with seven interrelated subsystems (Figure 18-1). Each subsystem is formed of a set of behavioral responses, or responsive tendencies, or action systems that share a common drive or goal. Organized around drives (some type of intra-organismic motivational structure), these responses are differentiated, developed, and modified over time through maturation, experience, and learning. They are determined developmentally and are governed continuously by a multitude of physical, biological, and psychological factors operating in a complex and interlocking fashion. Each subsystem can be described and analyzed in terms of structural and functional requirements. The four structural elements that have been identified include the following: (1) drive or goal—the ultimate consequence of behaviors in it; (2) set—a tendency or predisposition to act in a certain way. Set is subdivided into two types: preparatory, or what a person usually attends to, and perseverative, the habits that one maintains in a situation; (3) choice—represents the behavior a patient sees herself as being able to use in any given situation; and (4) action—or the behavior of an individual (Grubbs, 1980; Johnson, 1980). Set plays a major role both in the choices persons consider and in their ultimate behavior. Each of the seven subsystems has the same three functional requirements: (1) protection, (2) nurturance, and (3) stimulation. These functional requirements must be met through the person’s own efforts, or with the outside assistance of the nurse. For the subsystems to develop and maintain stability, each must have a constant supply of these functional requirements that usually are supplied by the environment. However, during illness or when the potential for illness poses a threat, the nurse may become a source of functional requirements. The responses by the subsystems are developed through motivation, experience, and learning and are influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors (Johnson, 1980). The behavioral system attempts to achieve balance by adapting to internal and environmental stimuli. The behavioral system is made up of “all the patterned, repetitive, and purposeful ways of behaving that characterize each man’s life” (Johnson, 1980, p. 209). This functional unit of behavior “determines and limits the interaction of the person and his environment and establishes the relationship of the person with the objects, events, and situations in his environment” (Johnson, 1980, p. 209). “The behavioral system manages its relationship with its environment” (Johnson, 1980, p. 209). The behavioral system appears to be active and not passive. The nurse is external to and interactive with the behavioral system. A state of instability in the behavioral system results in a need for nursing intervention. Identification of the source of the problem in the system leads to appropriate nursing action that results in the maintenance or restoration of behavioral system balance (Brown, 2006). Nursing interventions can occur in such general forms as (1) repairing structural units; (2) temporarily imposing external regulatory or control measures; (3) supplying environmental conditions or resources; or (4) providing stimulation to the extent that any problem can be anticipated, and preventive nursing action is in order (Johnson, 1978). “If the source of the problem has a structural stressor, the nurse will focus on either the goal, set, choice, or action of the subsystem. If the problem is one of function, the nurse will focus on the source and sufficiency of the functional requirements since functional problems originate from an environmental excess or deficiency” (Grubbs, 1980, p. 242). The goal of nursing is to maintain or restore the person’s behavioral system balance and stability, or to help the person achieve a more optimum level of behavioral system functioning when this is desired and possible (Johnson, 1978). The utility of the Johnson Behavioral System Theory is evident from the variety of clinical settings and age groups in which the theory has been used. It has been used in inpatient, outpatient, and community settings, as well as in nursing administration. It has been used with a variety of client populations, and several practice tools have been developed (Fawcett, 2005). Johnson does not use the term nursing process. Assessment, disorders, treatment, and evaluation are concepts referred to in a variety of Johnson’s works. “For the practitioner, conceptual models provide a diagnostic and treatment orientation, and thus are of considerable practical import” (Johnson, 1968, p. 2). The nursing process becomes applicable in the Behavioral System Model when behavioral malfunction occurs “that is in part disorganized, erratic, and dysfunctional. Illness or other sudden internal or external environmental change is most frequently responsible for such malfunctions” (Johnson, 1980, p. 212). “Assistance is appropriate at those times the individual is experiencing stress of a health-illness nature which disturbs equilibrium, producing tension” (Johnson, 1961a, p. 6). However, it is important to note that systems analysis is an important component of systems theory. One monitors outputs from a given subsystem in order to monitor performance. Signs of disequilibrium require one to identify the problem, to further define the problem by gathering data, and to design an intervention to restore equilibrium/balance (Miller, 1965; Jenkins, 1969). Johnson (1959a) implied that the initial nursing assessment begins when the cue tension is observed and signals disequilibrium. Sources for assessment data include history taking, testing, and structural observations (Johnson, 1980). “The behavioral system is thought to determine and limit the interaction between the person and his environment” (Johnson, 1968, p. 3). This suggests that the accuracy and quantity of the data obtained during nursing assessment are not controlled by the nurse, but by the patient (system). The only observed part of the subsystems structure is behavior. Six internal and external regulators have been identified that “simultaneously influence and are influenced by behavior,” including biophysical, psychological, developmental, sociocultural, family, and physical environmental regulators (Randell, 1991, p. 157). The nurse must be able to access information related to goals, sets, and choices that make up the structural subsystems. “One or more of [these] subsystems is likely to be involved in any episode of illness, whether in an antecedent or a consequential way or simply in association, directly or indirectly with the disorder or its treatment” (Johnson, 1968, p. 3). Accessing the data is critical to accurate statement of the disorder. Johnson did not define specific disorders, but she did state two general categories of disorders on the basis of their relationship to the biological system (Johnson, 1968). Disorders are those which are related tangentially or peripherally to disorder in the biological system; that is, they are precipitated simply by the fact of illness or the situational context of treatment; and…those [disorders] which are an integral part of a biological system disorder in that they are either directly associated with or a direct consequence of a particular kind of biological system disorder or its treatment (Johnson, 1968, p. 7). The “means of management” or interventions do consist in part of the provision of nurturance, protection, and stimulation (Johnson, 1968, 1980). The nurse may provide “temporary imposition of external regulatory and control mechanisms, such as inhibiting ineffective behavioral responses, and assisting the patient to acquire new responses” (Johnson, 1968, p. 6). Johnson (1980) suggested that techniques include “teaching, role modeling, and counseling” (p. 211). If a problem or a disorder is anticipated, preventive nursing action is appropriate with adequate methods (Johnson, 1980). Nurturance, protection, and stimulation are as important for preventive nursing care or health promotion as they are for managing illness (Brown, 2006). The outcome of nursing intervention is behavioral system equilibrium. “More specifically, equilibrium can be said to have been achieved at that point at which the individual demonstrates a degree of constancy in his pattern of functioning, both internally and interpersonally” (Johnson, 1961a, p. 9). The evaluation of the nursing intervention is based on whether it made “a significant difference in the lives of the persons involved” (Johnson, 1980, p. 215). The Behavioral System Model has been operationalized through the development of several assessment instruments. In 1974, Grubbs (1980) used the theory to develop an assessment tool and a nursing process sheet based on Johnson’s seven subsystems. Questions and observations related to each subsystem provided tools with which to collect important data that assist in discovery of other choices of behavior that will enable the patient to accomplish his or her goal of health. That same year, Holaday (1980) used the theory as a model to develop an assessment tool when caring for hospitalized children. This tool allowed the nurse to describe objectively the child’s behavior and to guide nursing action. In expanding the concept of “set,” Holaday also identified patterns of maternal behaviors that would indicate an inadequate or poorly functioning set that was eroding to the limited choices of action in responding to the needs of chronically ill infants (1981, 1982). Derdiarian (1990) investigated patient and nurse satisfaction using two systematic assessment instruments. The Johnson Behavioral System Model was used to develop a self-report and observational instrument to be implemented with the nursing process. The Derdiarian Behavioral System Model instrument included assessment of the restorative subsystem and the seven subsystems advocated by Johnson. The results indicated that implementation of the instruments provided a more comprehensive and systematic approach to assessment and intervention, thereby increasing patient and nurse satisfaction with care. Lanouette and St-Jacques (1994) used Johnson’s model to compare the coping abilities and perceptions of families with premature infants with those of families with full-term infants. The results indicated that positive coping skills were relative to bonding with the infant, using resources, solving problems, and making decisions. Lanouette and St-Jacques suggested that improvement in nursing care practices in nursery, hospital, and community settings might have contributed to this outcome. This supported Johnson’s (personal correspondence, 1996) statement that “the effective use of nurturance, protection, and stimulation during maternal contact at birth could significantly reduce the behavioral system problems we see today.” Case studies have documented the use and evaluation of the Johnson Behavioral System Model in clinical practice. In 1980, Rawls used the theory to assess systematically a patient who was facing the loss of function in one arm and hand. Herbert (1989) reported the outcomes of a nursing care plan developed for an elderly stroke patient. Rawls and Herbert concluded that Johnson’s theory provided a theoretical base that predicted the results of nursing interventions, formulated standards for care, and administered holistic care. Fruehwirth (1989) found it equally effective in assessing and intervening with a support group for the caregivers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Recent studies of nursing practice using Johnson’s model have focused on decision making and evaluation of outcomes. Grice (1997) found that the nurse, the patient, and the situational characteristics influenced assessment and decision making for the administration of antianxiety and antipsychotic medication to psychiatric inpatients at certain hours. Benson (1997) conducted a review of research literature on the fear of crime among older adults. The Behavioral System Model was used to describe the “hazards of fear of crime” that could cause disturbances in the ingestive, dependency, achievement, affiliative, and aggressive-protective subsystems (Benson, 1997, p. 26). Patient- and communityfocused interventions were presented to improve quality of care and the quality of life of older adults. Brinkley, Ricker, and Toumey (2007) demonstrated the use of the Johnson Behavioral System Theory with a morbidly obese patient with complex needs. Lachicotte and Alexander (1990) examined the use of Johnson’s Behavioral System Model as a framework for nursing administrators to use when making decisions concerning the management of impaired nurses. They suggested that, by viewing all levels of the environment, the framework encouraged nurse administrators to assess the imbalance in the nursing system when nurse impairment exists, and evaluate the “system’s state of balance in relationship to the method chosen to deal with nurse impairment” (Lachicotte & Alexander, 1990, p. 103). The results of the study indicated that nurse administrators preferred an assistive approach when dealing with nurse impairment. It was believed that “when the impaired nurse is confronted and assisted, equilibrium begins to be restored and balance brought back to the system” (Lachicotte & Alexander, 1990, p. 103). At the University of California, Los Angeles, the Neuropsychiatric Institute and Hospital has used Johnson’s Behavioral System Model for many years as the basis for their psychiatric nursing practice (Auger & Dee, 1983; Poster et al., 1997). “Patients are assessed and behavioral data are classified by subsystem. Nursing diagnoses are formulated that reflect the nature of the ineffective behavior and its relationship to the regulators in the environment” (Randell, 1991, p. 154). The use of Johnson’s theory is also incorporated into the new graduate orientation program (Puntil, 2005). A study comparing the diagnostic labels generated from the Johnson Behavioral System Model with those on the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association list indicated that the Johnson Behavioral System Model was better at distinguishing the problems and the etiology (Randell, 1991). It has become increasingly important to document nursing care and to demonstrate the effectiveness of the care on patient outcomes. Using Johnson’s model, Poster and colleagues (1997) found a positive relationship between nursing interventions and the achievement of patient outcomes at discharge. They concluded that “a nursing theoretical framework made it possible to prescribe nursing care as a distinction from medical care” (Poster et al., 1997, p. 73). Dee, van Servellen, and Brecht (1998) examined the effects of managed health care on patient outcomes, using Johnson’s Behavioral System Model. Upon admission, nurses develop a behavioral profile by assessing the eight subsystems, determine the balance or imbalance of the subsystems, and rate the impact of the six regulators. This profile is used to determine the nursing diagnoses, plan of action, and evaluation of care for each patient. The results of this study indicated significant improvement in the level of functioning upon discharge for patients with shorter hospital stays. Loveland-Cherry and Wilkerson (1983) analyzed Johnson’s theory and concluded that it has utility in nursing education. A curriculum based on a person as a behavioral system would have definite goals and straightforward course planning. Study would center on the patient as a behavioral system and on its dysfunction, which would require use of the nursing process. In addition to an understanding of systems theory, the student would need knowledge from the social and behavioral disciplines and the physical and biological sciences. The model has been used in practice and in educational institutions in the United States, Canada, and Australia (Derdiarian, 1981; Fleming, 1990; Grice, 1997; Hadley, 1970; Harris, 1986; Orb & Reilly, 1991; Puntil, 2005).
Behavioral System Model
CREDENTIALS AND BACKGROUND OF THE THEORIST
THEORETICAL SOURCES
USE OF EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE
MAJOR ASSUMPTIONS
Nursing
Person
Health
Environment
THEORETICAL ASSERTIONS
ACCEPTANCE BY THE NURSING COMMUNITY
Practice
Education
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

