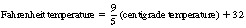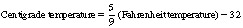Chapter 3 Basic chemistry of body fluids and electrolytes
Metric system
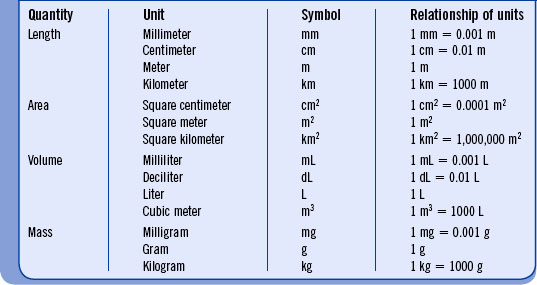
A solid review of the basic system of measurement is necessary because the metric system is used in chemical and physical measurements that relate to body physiology. Length is expressed by the basic unit of the meter. The basic unit of mass is the gram, and the liter is the basic unit of volume. Table 3-1 lists common metric terms and their interrelationship.
The metric system is entirely decimal. Prefixes indicate smaller or larger units (Table 3-2).
Table 3-2 Metric Decimal Prefixes
| Multiplication factors | Prefix | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 0.1 = 10–1 | deci | d |
| 0.01 = 10–2 | centi | c |
| 0.001 = 10–3 | milli | m |
| 0.000001 = 10–6 | micro | μ |
| 0.000000001 = 10–9 | nano | n |
| 0.000000000001 = 10–12 | pico | p |
To relate the metric system to more familiar uses, the following approximations may be helpful:
• 1 meter (m) = 39.37 inches (in)
• 1 inch (in) = 2.54 centimeters (cm)
• 1 liter (L) = 1.057 quarts (U.S.) (qt)
• 1 gallon (gal) = 3.785 liters (L)
• 1 kilogram (kg) = 2.2 pounds (lb)
• 1 ounce (oz) = 28.35 grams (g)
Temperature is expressed in degrees centigrade. Zero degrees centigrade is the freezing point of water and 100°C is its boiling point. The following is a comparison of some centigrade temperatures with the Fahrenheit scale:
| °F | °C | |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling point of water | 212 | 100 |
| Normal body temperature | 98.6 | 37 |
| Freezing point of water | 32 | 0 |
For conversion of Fahrenheit values to centigrade and vice versa, use the formula:
What is atomic weight?
Atomic weights relate to one another based on an arbitrary scale that assigns a weight of 12 atomic mass units (amu) to the carbon isotope 12 (12C). On this scale, protons and neutrons each weigh 1 amu; electrons have negligible mass. The hydrogen atom (1H) is 1 amu, and the oxygen atom (16O) is 16 amu. One atomic mass unit is sometimes called a dalton (Da), after John Dalton, an early developer of the atomic concept.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree