Chapter 6 Admission emergencies
MANAGEMENT OF IMMINENT DELIVERY WITH OR WITHOUT FETAL COMPROMISE
The following procedures should be adopted if delivery is imminent.
SPECIFIC PROBLEMS
Cord presentation or prolapse
Always confirm gestational age before planning any further management.
Cord presentation
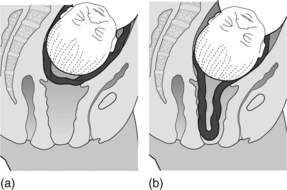
This occurs when the cord is in front of the presenting part of the fetus behind intact membranes. When the membranes are not ruptured, palpate through them with the tip of the fingers to exclude the presence of pulsation due to cord presentation or vasa praevia (Figure 6.1a). The diagnosis can also be made using ultrasound and colour flow Doppler, and is useful in circumstances such as an unstable breech presentation. Variable fetal heart rate decelerations may be evident.
Cord prolapse
Following membrane rupture the cord may prolapse through the cervix, may remain in the vagina or be expelled through the introitus (Figure 6.1b).
Cord prolapse occurs in approximately 0.2% of all births.
Points to remember in management
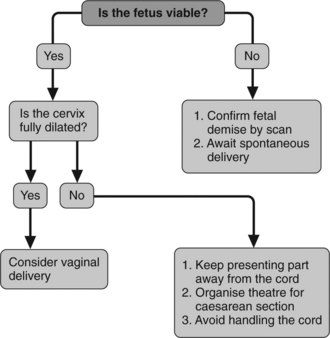
Figure 6.2 presents an algorithm for management of cord prolapse.
Major obstetric haemorrhage
Management
Box 6.1 gives details of blood component therapy.
Box 6.1 Blood component therapy