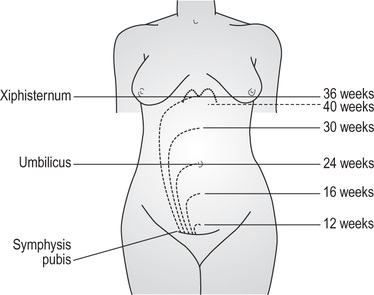
abduct to draw away from axis or median plane. abduction drawing away from centre, e.g. abduction of mother’s legs for vaginal delivery. aberrant wandering or deviating from normal site or course. abort to bring to premature end, especially pregnancy. abortifacient chemical or surgical means of causing abortion, miscarriage. abrachia congenital absence of arms. abreaction reliving experience so previously repressed associated emotions are released. abuse deliberate inflicting of physical, emotional or sexual injury, trauma, pain on individual. accountable liable to be held responsible for course of action. ACE inhibitors See angiotensin. acetabulum cup-shaped socket in pelvic innominate bone into which head of femur fits. acetoacetic acid product of abnormal fat metabolism, occurring in diabetic and dehydrated mothers. aciclovir, acyclovir antiviral agent to treat herpes simplex, orally or intravenously. acridine orange stain used in fluorescence microscopy; causes bacteria to fluoresce green to red. acromion process of scapula, forming point of shoulder. adactylia, adactyly congenital absence of fingers or toes. addiction physiological or psychological dependence, e.g. alcohol or drugs. adduct to draw towards centre or median line. adnexa appendages. Uterine a. ovaries and fallopian tubes. adolescence developmental stage from puberty to cessation of physical growth. adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) anterior pituitary gland hormone that stimulates adrenal cortex. adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) See respiratory distress syndrome. Advanced Life Support in Obstetrics (ALSO) specialist training courses for midwives, doctors, other staff; cover advanced methods of dealing with emergency situations. See appendices 1,2,3. aerobe organism requiring air or free oxygen to sustain life. Adj aerobic. aetiology science of causes, e.g. of disease. afibrinogenaemia absence of fibrinogen in blood; hypofibrinogenaemia. afterbirth lay term for placenta and membranes expelled from uterus after birth of baby. aftercoming head fetal head (coming after trunk) in breech delivery. See breech. agglutinin substance that reacts with agglutinogen, causes agglutination to occur. agglutinogen substance that stimulates specific agglutinin to cause agglutination. agnathia failure of jaw development. AIDS See acquired immune deficiency syndrome. ala wing, e.g. sacral ala. Pl alae. alba, albicans white. Linea a. white line in midline of abdomen in Caucasians.
A
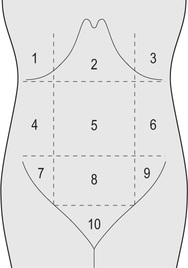
1, Right hypochondrium; 2, epigastrium; 3, left hypochondrium; 4, right lumbar region; 5, umbilical region; 6, left lumbar region; 7, right iliac fossa; 8, hypogastrium; 9, left iliac fossa; 10, suprapubis.
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access