Skill 84
Wound Drainage Devices
Jackson-Pratt, Hemovac
If drainage accumulates in the wound bed, wound healing is delayed. Drainage is removed by using either a closed or an open drain system even if the amount of drainage is small. An open drain system (e.g., a Penrose drain [Fig. 84-1]) removes drainage from the wound and deposits it onto the skin surface. Insert a sterile safety pin through the drain, outside the skin, to prevent the tubing from moving into the wound. To remove the Penrose drain, the health care provider advances the tubing in stages as the wound heals from the bottom up.
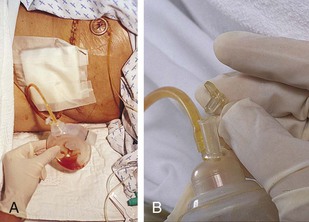
A closed drain system, such as the Hemovac drain (Fig. 84-2) or Jackson-Pratt (JP) drain (Fig. 84-3), relies on the presence of a vacuum to withdraw accumulated drainage from around the wound bed into the collection device. The collection device is connected to a clear plastic drain with multiple perforations. Drainage collects in a closed reservoir, or a suction bladder.
Delegation Considerations
The assessment of wound drainage and maintenance of drains and the drainage system cannot be delegated to NAP. However, you may delegate emptying a closed drainage container or pouch, measuring the amount of drainage, and reporting the amount on the patient’s intake and output (I&O) record to NAP. The nurse directs the NAP by:
▪ Discussing any increase in frequency of emptying the drain other than once a shift.
▪ Instructing to report to the nurse any change in amount, color, or odor of drainage.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree