Skill 81
Urinary Diversion
Pouching an Incontinent Urinary Diversion
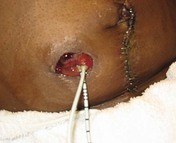
Because urine flows continuously from an incontinent urinary diversion, placement of the pouch is more challenging than with the fecal diversion. In the immediate postoperative period urinary stents extend out from the stoma (Fig. 81-1). A surgeon places the stents to prevent stenosis of the ureters at the site where the ureters are attached to the conduit. The stents will be removed during the hospital stay or at the first postoperative visit with the surgeon. The stoma is normally red and moist. It is made from a portion of the intestinal tract, usually the ileum. It should protrude above the skin. An ileal conduit is usually located in the right lower quadrant. While the patient is in bed, the pouch may be connected to a bedside drainage bag to decrease the need for frequent emptying. When the patient goes home, the bedside drainage bag may be used at night to avoid having to get up to empty the pouch. Each type of urostomy pouch comes with a connector for the bedside drainage bag.
Delegation Considerations
The skill of pouching a new incontinent urinary diversion cannot be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). In some agencies, care of an established urostomy (4 to 6 weeks or more after surgery) can be delegated to NAP. The nurse directs the NAP about:
▪ Expected appearance of the stoma.
▪ Expected amount and character of the output and when to report changes.
▪ Changes in patient’s stoma and surrounding skin integrity that should be reported.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree