Skill 63
Respiration Assessment
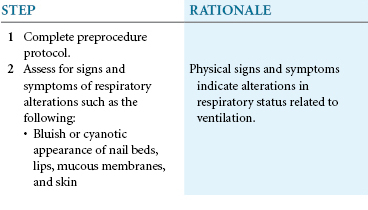
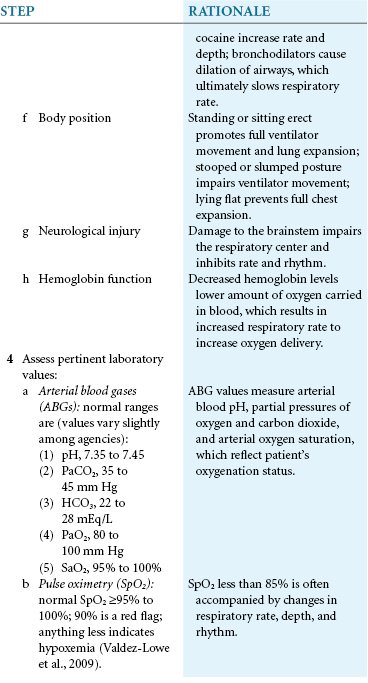
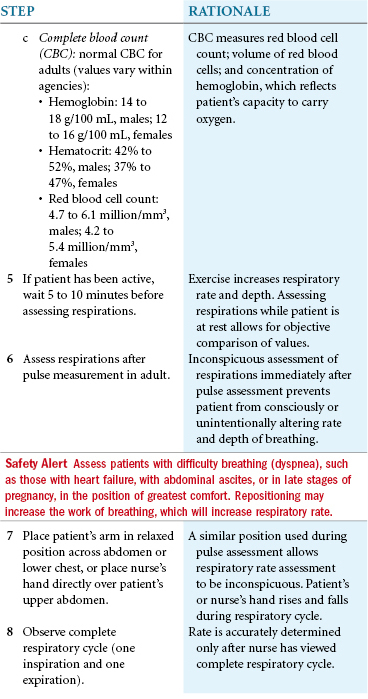
You assess ventilation by observing the rate, depth, and rhythm of respiratory movements. Accurate assessment of respiration depends on recognizing normal thoracic and abdominal movements. Normal breathing is both active and passive. On inspiration, the diaphragm contracts, and the abdominal organs move down to increase the size of the chest cavity. At the same time the ribs and sternum lift outward to promote lung expansion. On expiration, the diaphragm relaxes upward, and the ribs and sternum return to their relaxed position. Expiration is an active process only during exercise, with voluntary hyperventilation, and in the presence of certain disease states.
Delegation Considerations
The skill of counting respirations can be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP) unless the patient is considered unstable (i.e., complains of dyspnea). The nurse instructs the NAP by: