Drugs Used to Treat Cancer
Objectives
1 Identify common sites for cancer in men and women and cite the goals of chemotherapy.
2 Cite the rationale for giving chemotherapeutic drugs on a precise time schedule.
4 Describe the role of targeted anticancer agents in treating cancer.
5 Describe the role of chemoprotective agents in treating cancer.
6 Describe the role of bone marrow stimulants in treating cancer.
Key Terms
cancer ( ) (p. 698)
) (p. 698)
metastases ( ) (p. 698)
) (p. 698)
cell cycle–specific ( ) (p. 698)
) (p. 698)
cell cycle–nonspecific ( ) (p. 698)
) (p. 698)
palliation (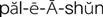 ) (p. 699)
) (p. 699)
combination therapy (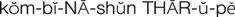 ) (p. 699)
) (p. 699)
targeted anticancer agents (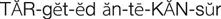 ) (p. 707)
) (p. 707)
chemoprotective agents ( ) (p. 707)
) (p. 707)
Cancer and the Use of Antineoplastic Agents
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Clayton
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Clayton
Cancer is a disorder of cellular growth, life span, and death. It is a group of abnormal cells that generally proliferate (multiply) more rapidly than normal cells, lose the ability to perform specialized functions, invade surrounding tissues, and develop growths in other tissues distant to the site of original growth (metastases). Many types of cancer cells also lose the ability to die normally as a part of their life cycle. Normal cells have a genetically programmed life cycle that includes a cell death known as apoptosis.
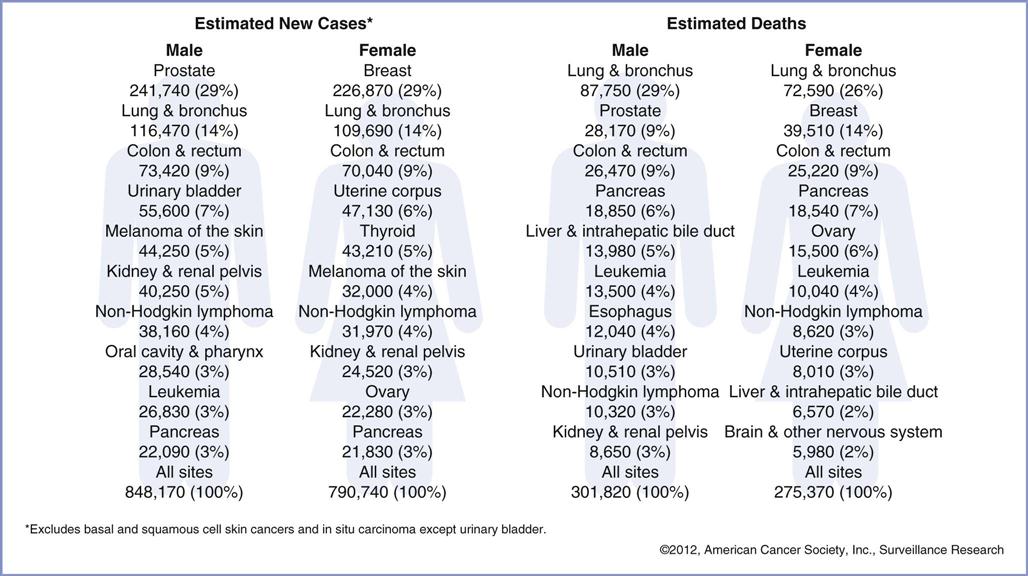
Cancer is a leading cause of death in the United States. Unfortunately, the number of people that die from malignant diseases increases each year. The American Cancer Society estimates new cancer cases in Facts and Figures annually as a means of projecting cancer incidence for the upcoming year (Figure 44-1). Early diagnosis and treatment is still one of the most important factors in providing a more optimistic prognosis for those patients stricken with the many forms of neoplastic disease.
Treatment of cancer often requires a combination of surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Recent advancements in carcinogenesis, cellular and molecular biology, and tumor immunology have enhanced the role that antineoplastic agents may play in therapy. It is beyond the scope of this chapter to delve into the interrelationships of chemotherapy and neoplastic disease; however, a short discussion of the concepts of cancer chemotherapy will be presented. As a result of rapidly changing approaches to the treatment of specific malignancies and the changing nature of chemotherapeutic regimens, specific agents and dosages will not be discussed.
All cells, whether normal or malignant, pass through a similar series of phases during their lifetime, although duration of time spent in each phase differs with the type of cell (Figure 44-2). Mitosis is the phase of cellular proliferation in which the cell divides into two equal daughter cells. Cells either advance into a nonproliferative stage, known as G0, or advance to the first gap phase, G1. G0 is the largest variable in the cell cycle, and during this resting phase the cell is not actively replicating. Some stimulus results in the cell entering the G1 phase. Phase G1 is considered a presynthetic phase in which the cell prepares for DNA synthesis by manufacturing necessary enzymes. The S phase is the stage of active synthesis of two sets of DNA. Phase G2 is a postsynthetic phase in which the cell prepares for mitosis by producing ribonucleic acid (RNA), specialized proteins, and the foundations for mitotic spindle apparatus needed for mitosis. The cell cycle begins again when the mitotic phase divides the cell into two daughter cells. The daughter cells may advance again to the G1 phase or pass into G0. The time required to complete one cycle is termed the generation time.
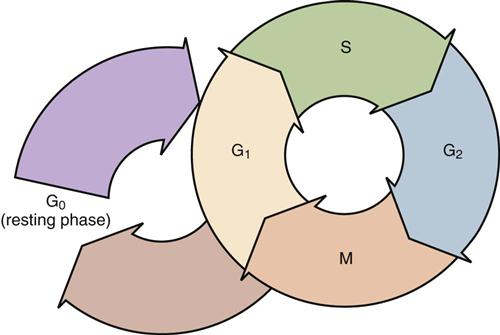
Many antineoplastic agents are cell cycle–specific (i.e., the drug is selectively toxic when the cell is in a specific phase of growth, and therefore is schedule-dependent). Malignancies most amenable to cell cycle–specific chemotherapy are those that proliferate rapidly. Cell cycle–nonspecific drugs are active throughout the cell cycle and may be more effective against slowly proliferating neoplastic tissue. These agents are not schedule-dependent but are dose-dependent. One implication of cell cycle specificity is the importance of correlating the dosage schedule of anticancer therapy with the known cellular kinetics of that type of neoplasm. Drugs are usually administered when the cell is most susceptible to the cytotoxic effects of the agent for a higher “kill rate” of neoplastic cells. Table 44-1 lists the more common commercially available drugs, their general dosage ranges, major toxicities, and major indications.
![]() Table 44-1
Table 44-1
Cancer Chemotherapeutic Agents
| DRUG | USUAL DOSAGE, ROUTE, AND FREQUENCY | TOXICITY | MAJOR INDICATIONS | |
| ACUTE | DELAYED | |||
| Alkylating Agents | ||||
| IV: 100 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of a 28-day cycle, up to six cycles | Fever, nausea, vomiting | Moderate depression of peripheral blood count | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | |
| PO: 4-8 mg/day for 2-3 wk, stop for recovery, then maintenance | Edema | Bone marrow depression | Chronic myelogenous leukemia | |
| 360 mg/m2 q 4 wk as a single agent | Nausea, vomiting | Bone marrow suppression, anemia, nephrotoxicity | Ovarian carcinoma | |
| As single agent: IV: 150-200 mg/m2 over 1- to 2-hr infusion q 6 wk In combination: Dosage individualized Caution: Use gloves because solution may cause skin discoloration | Nausea and vomiting; pain along vein of infusion | Granulocyte and platelet suppression; hepatic, pulmonary, renal toxicity | Brain tumors, Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, multiple myeloma, malignant melanoma | |
| PO: Start 0.1-0.2 mg/kg/day; adjust for maintenance | None | Bone marrow depression (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) can be severe with excessive dosage | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphosarcoma, Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | |
| IV: 20-100 mg/m2; frequency highly variable depending on cancer being treated | Nausea, vomiting | Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, blurred vision, changes in color perception | Testicular and ovarian cancers, bladder cancer | |
| IV: 40-50 mg/kg in divided doses over 2-5 days PO: 1-5 mg/kg/day for variable duration; adjust for maintenance | Nausea and vomiting | Bone marrow depression, alopecia, cystitis | Hodgkin’s disease and other lymphomas, multiple myeloma, lymphocytic leukemia, many solid cancers | |
| IV: 2-4.5 mg/kg/day for 10 days; repeat q 28 days IV: 150 mg/m2 daily for 5 days in 4-wk cycles | Nausea and vomiting, flu-like syndrome | Bone marrow depression (rare) | Metastatic malignant melanoma, Hodgkin’s disease | |
| IV: 1.2 g/m2/day for 5 days | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Hematuria, alopecia, confusion, coma | Testicular, lung, breast, ovarian, pancreatic, gastric cancer | |
| PO: 100-130 mg/m2 once q 6 wk | Severe nausea and vomiting; anorexia | Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, alopecia, confusion, lethargy, ataxia | Brain tumors, Hodgkin’s disease | |
| IV: 0.4 mg/kg in single or divided doses over 2 days | Nausea and vomiting | Moderate depression of peripheral blood count | Hodgkin’s disease and other lymphomas, bronchogenic carcinoma | |
| PO: 0.2 mg/kg/day for 5 days; 2-4 mg/day as maintenance or 0.1-0.15 mg/kg/day for 2-3 wk | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Bone marrow depression | Multiple myeloma, ovarian carcinoma, testicular seminoma | |
| IV: 85 mg/m2; used in combination with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil | Diarrhea, emesis, fatigue | Anemia, peripheral sensory neuropathy, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia | Colon cancer | |
| As single agent: daily schedule—500 mg/m2 for 5 consecutive days q 6 wk; weekly schedule—1000 mg/m2 at weekly intervals for 2 wk; assess response Adjust dosage according to response. | Hypoglycemia, severe nausea, vomiting | Moderate but transient renal and hepatic toxicity, hypoglycemia, mild anemia, leukopenia | Pancreatic islet cell carcinoma | |
| PO: 150 mg/m2 once daily for 5 days per 28-day cycle | Headache, nausea, vomiting, constipation | Bone marrow depression, seizures | Glioblastoma, astrocytoma | |
| IV: 0.3-0.4 mg/kg q 1-4 wk | Dizziness, headache, anorexia | Bone marrow depression | Hodgkin’s disease, ovarian, breast, and bladder carcinoma | |
| Antimetabolites | ||||
| 1250 mg/m2 twice daily for 2 wk, followed by 1 wk of rest | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue | Bone marrow depression, dermatitis, hand-and-foot syndrome, lymphopenia | Breast cancer, colorectal cancer | |
| IV: 0.09-0.1 mg/kg/day infused over 24 hr for 7 consecutive days | Headache, dizziness, rash, nausea | Bone marrow depression, purpura | Hairy cell leukemia, lymphomas | |
| IV: 52 mg/m2 over 2 hr daily for 5 days | Flushing, hypotension, hypertension, headache, nausea, vomiting | Bone marrow depression, dermatitis | Acute lymphocytic leukemia | |
| Highly variable for condition being treated | Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, oral ulceration | Bone marrow depression, megaloblastosis | Acute leukemias | |
| IV: 15 mg/m2 over 3 hr, repeated q 8 hr for 3 days The cycle is repeated q 6 wk for a minimum of four cycles if tolerated | Nausea, fever, fatigue, cough, diarrhea | Hyperglycemia, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, petechiae | Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) | |
| 0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg/day by intra-arterial infusion using an implantable pump | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia; hepatotoxicity | GI adenocarcinoma metastatic to the liver; tumors of the liver, ovaries, and kidneys | |
| 25 mg/m2 daily for 5 days; start q 5-day cycle q 28 days | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, myalgia | Edema, rash, weakness, cough, dyspnea, hemolytic anemia | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, other leukemias | |
| IV: 12 mg/kg/day for 4 days, then 6 mg/kg/day on the 6th, 8th, 10th, and 12th days | Nausea | Oral and GI ulceration, stomatitis and diarrhea, bone marrow depression | Breast, large bowel, ovarian, pancreatic, stomach carcinoma | |
| IV: 1250 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 of q 21-day cycle | Nausea, vomiting | Bone marrow suppression, rashes, edema | Pancreatic, ovarian, breast, lung cancer | |
| PO: 2.5 mg/kg/day for induction then 1.5 to 2.5 mg/kg/day as maintenance | Occasional nausea, vomiting; usually well tolerated | Bone marrow depression, occasional hepatic damage | Acute lymphocytic leukemia; acute myelogenous leukemia | |
| Highly variable for condition being treated | Occasional diarrhea, hepatic necrosis | Oral and GI ulceration, bone marrow depression (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia), cirrhosis | Acute lymphocytic leukemia, choriocarcinoma, carcinoma of cervix and head and neck area, mycosis fungoides, solid cancers | |
| IV: 500 mg/m2 over 10 min on day 1 of q 21-day cycle | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Bone marrow depression, renal dysfunction | Malignant pleural mesothelioma, non–small cell lung cancer | |
| IV: 4 mg/m2 over 20-30 min every other wk | Nausea, vomiting, muscle pain, headache, bloating, constipation, diarrhea | Bone marrow depression, renal dysfunction | Hairy cell leukemia, lymphomas | |
| IV push: 30 mg/m2 over 3-5 min once weekly for 6 wk in 7-wk cycle | Fatigue, pruritus, constipation, nausea, vomiting, edema, nose bleeds | Bone marrow depression, mucositis | Peripheral T-cell lymphoma | |
| PO: 2 mg/kg/day | Occasional nausea, vomiting; usually well tolerated | Bone marrow depression | Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia | |
| Natural Products | ||||
| IV: 50-100 mg/m2 daily for 5 days; cycles of therapy are given q 3-4 wk | Nausea (30%-40%), vomiting, stomatitis, diarrhea | Leukopenia, nadir in 10-14 days, recovery in 3 wk; thrombocytopenia; alopecia | Testicular tumors, small cell carcinoma of the lung, Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, ovarian carcinoma, Kaposi’s sarcoma | |
| IV: 60-100 mg/m2 q 3 wk | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Bone marrow suppression, rashes, hypersensitivity | Breast cancer, prostate cancer; gastric adenocarcinoma, head and neck cancer; non–small cell lung cancer | |
| Different dosages for cancer being treated and regimen used | Nausea, vomiting, hypotension, diarrhea | Bone marrow suppression, mucositis, peripheral neuropathy | Ovarian carcinoma, breast carcinoma, AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma, lung cancer | |
(Vumon) | Variable based on other treatments | Diarrhea, nausea/vomiting | Bone marrow suppression, mucositis | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| IV: 3.7 mg/m2/wk or q 2 wk Dosage adjusted based on white cell count | Nausea, vomiting, local irritant | Alopecia, stomatitis, bone marrow depression, loss of reflexes | Hodgkin’s disease and other lymphomas, solid cancers | |
| IV: 1.4 mg/m2/wk once weekly | Local irritant | Areflexia, peripheral neuritis, paralytic ileus, mild bone marrow depression | Acute lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease and other lymphomas, solid cancers | |
| IV: 30 mg/m2/wk over 6-10 min once weekly | Nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea | Bone marrow suppression, hepatotoxicity, bronchospasm | Non–small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, cervical carcinoma, Kaposi’s sarcoma | |
| Antibiotics | ||||
| IM, IV, subcutaneous: 0.25-0.5 units/kg once or twice weekly | Nausea, vomiting, fever, very toxic | Edema of hands, pulmonary fibrosis, stomatitis, alopecia | Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck, testicular carcinoma | |
| Highly variable for condition being treated | Nausea, vomiting, local irritant | Stomatitis, oral ulcers, diarrhea, alopecia, mental depression, bone marrow depression | Testicular carcinoma, Wilms’ tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing’s and osteogenic sarcoma, and other solid tumors | |
| IV: 30-45 mg/m2/day for 2-3 days of combination therapy Never give IM or subcutaneously | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chills | Bone marrow suppression, reversible alopecia | Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia in adults; acute lymphocytic leukemia in children and adults | |
| IV: 60-75 mg/m2, single dose or over 3 days; repeat q 3 wk up to total dose 500 mg/m2 | Nausea, red urine (not hematuria) | Bone marrow depression, cardiotoxicity, alopecia, stomatitis | Soft tissue, osteogenic and miscellaneous sarcomas, Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, bronchogenic and breast carcinoma, thyroid cancer, leukemias | |
| IV: 100 to 120 mg/m2 once q 3- to 4-wk cycle | Nausea, vomiting, red urine (not hematuria), rash, diarrhea | Bone marrow depression, cardiotoxicity, alopecia, stomatitis | Breast cancer | |
| Slow IV: 12 mg/m2/day (10-15 min) for 3 days Never give IM or subcutaneously | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Bone marrow suppression, cardiotoxicity, mucositis, hemorrhage | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| Variable | Nausea, vomiting, flu-like syndrome | Bone marrow depression, skin toxicity; pulmonary, renal, CNS effects | Squamous cell carcinoma of cervix; adenocarcinoma of the stomach, pancreas, bladder cancer | |
| IV infusion: 12 mg on days 1 to 3, q 3 wk or q 3 mo | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Heart failure; GI bleeding; cough, dyspnea | Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, prostate cancer | |
| 800 mg q wk via urethral catheter into bladder | Bladder spasm, hematuria, abdominal pain | Rash | Carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder | |
| Other Synthetic Agents | ||||
| Variable | Confusion, dyspnea, nausea, diarrhea | Bone marrow depression, liver dysfunction | Melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, T-cell lymphoma | |
| PO: 260 mg/m2/day for 14 or 21 days in 28-day cycle Give daily dosage as four divided oral doses | Nausea, vomiting | Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, peripheral neuropathy | Ovarian cancer | |
| Subcutaneous: 240 mg as two injections of 120 mg at a concentration of 40 mg/mL; then 80 mg subcutaneously q 28 days | Chills, fatigue | Weight increase, back pain; injection site injury (pain, erythema, swelling) | Advanced prostate cancer | |
| IV: 9 or 18 mcg/kg/day for 5 consecutive days; q 21 days for eight cycles | Hypotension, dysrhythmias, dizziness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting | Vascular leak syndrome manifested by hypotension, edema, hypoalbuminemia; anemia, paresthesias | Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | |
| PO: 80 mg/kg as a single dose q 3 days or 20-30 mg/kg/day | Mild nausea, vomiting | Bone marrow depression | Chronic granulocytic leukemia, ovarian cancer, melanoma, carcinoma of the head and neck | |
| Variable | Flulike syndrome | Bone marrow depression | Hairy cell leukemia, Kaposi’s sarcoma, malignant melanoma, follicular lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia | |
| Subcutaneous: 1 mg daily IM, depot dosing range: 3.75-4.5 mg q 1-6 mo | Hot flashes; initial exacerbation of symptoms | Dysrhythmias, edema | Prostatic carcinoma, breast carcinoma; endometriosis | |
| 2-6 g/day in three or four divided doses, then increase incrementally to 9-10 g/day in three or four divided doses (maximum daily dose 18 g) | Nausea, vomiting | Dermatitis, diarrhea, mental depression | Adrenal cortical carcinoma | |
| Single agent treatment for Hodgkin’s disease: PO: start 2-4 mg/kg/day for the first week; increase over 1 wk to 4-6 mg/kg as maintenance until maximum response or hematological toxicity | Nausea, vomiting | Bone marrow depression, CNS depression | Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, lung cancer, melanoma | |
| IV: three complete doses at 2-wk intervals | Fatigue, chills, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting | Paresthesias, back pain, joint ache, pain in extremities | Prostate cancer | |
| Hormones | ||||
| PO: 1 mg daily | Nausea, vomiting, headache | Hot flashes, diarrhea, constipation, pelvic pain, edema | Breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following tamoxifen therapy | |
| PO: 50 mg daily (use with luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone [LHRH] analog) | Nausea, constipation, peripheral edema, diarrhea | Hepatitis, gynecomastia, dyspnea | Prostate cancer | |
| 14 mg/kg/day in three or four divided doses Take with water No calcium-rich products | Nausea, diarrhea | Thrombosis, hyperglycemia, hepatic dysfunction, breast tenderness | Prostate cancer | |
| Prostate: PO: 1-2 mg three times daily Breast: PO: 10 mg three times daily | None | Fluid retention, hypercalcemia, feminization, uterine bleeding | Breast and prostate carcinomas | |
| 25 mg daily after a meal | Nausea, fatigue, insomnia | Depression, anxiety, hot flashes, dyspnea | Breast cancer in postmenopausal women, with disease progression following tamoxifen therapy | |
| PO: 10-40 mg/day in divided doses | None | Fluid retention, masculinization, cholestatic jaundice | Breast carcinoma | |
| PO: 250 mg three times daily at 8-hr intervals (total daily dose is 750 mg) | Nausea, vomiting | Hot flashes, loss of libido, impotence, gynecomastia, hepatotoxicity | Metastatic prostatic carcinoma | |
| IM: 500 mg in buttocks (one 250 mg injection in each buttock) on days 1, 15, 29, and then once monthly thereafter | Nausea, headache, constipation | Dyspnea, rash | Breast cancer | |
| Subcutaneous implant: 3.6 mg q 28 days in upper abdominal wall Local anesthesia may be used | Anorexia, dizziness, pain | Hot flashes, sexual dysfunction | Prostate and breast cancer | |
| Subcutaneous implant: 50 mg in inner aspect of upper arm q 12 mo | Insertion site reaction | Hot flashes, gynecomastia, fatigue | Prostate cancer | |
| PO: 2.5 mg daily | Nausea, vomiting, headache | Muscle aches, hot flashes, constipation, diarrhea, fatigue | Breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following antiestrogen therapy | |
| IM: 400-1000 mg/wk | None | None | Endometrial carcinoma, renal cell, breast cancer | |
| PO: 300 mg once daily for 30 days, then 150 mg daily | Insomnia, headache, nausea, constipation | Hot flashes, impaired adaptation to dark | Prostate cancer | |
| 20-40 mg daily in two divided doses | Nausea, vomiting, hot flashes | Increased bone and tumor pain, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, edema, hypercalcemia | Breast cancer (estrogen sensitive) | |
| IM: 200-400 mg q 2-4 wk | None | Fluid retention, masculinization | Breast carcinoma | |
| PO: 60 mg daily | Nausea, vomiting | Hot flashes, sweating, vaginal discharge | Metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women with estrogen-positive tumors | |
| Depot: 3.75 mg IM: q 28 days | Vomiting, fatigue | Hot flashes, impotence, insomnia | Prostate cancer | |
| IM: Long-impacting: 11.25 mg q 84 days, or 22.5 mg q 24 wk | Vomiting, fatigue | Hot flashes, impotence, insomnia | Prostate cancer | |
| DNA Topoisomerase Inhibitors | ||||
| Variable depending on regimen | Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea, constipation, shortness of breath | Diarrhea, bone marrow suppression, alopecia | Carcinoma of the colon and rectum | |
| IV: 2.3 mg/m2 over 30 min for 5 days of a 21-day course | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath | Alopecia, bone marrow depression, stomatitis | Small cell lung cancer | |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree