Skill 33
Intradermal Injections
You typically give intradermal (ID) injections for skin testing (e.g., tuberculosis screening and allergy tests). Because such medications are potent, you inject them into the dermis, where blood supply is reduced and drug absorption occurs slowly. A patient may have an anaphylactic reaction if the medications enter the circulation too rapidly. Skin testing often requires you to visually inspect the test site; therefore make sure that the ID sites are free of lesions and injuries and relatively hairless. The inner forearm and upper back are ideal locations. To administer an ID injection, use a tuberculin (TB) or small syringe with a short (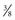 to
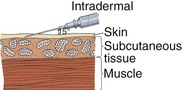
to 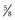 inch), fine-gauge (25 to 27) needle. The angle of insertion for an intradermal injection is 5 to 15 degrees (Fig. 33-1). Inject only small amounts of medication (0.01 to 0.1 mL) intradermally.
inch), fine-gauge (25 to 27) needle. The angle of insertion for an intradermal injection is 5 to 15 degrees (Fig. 33-1). Inject only small amounts of medication (0.01 to 0.1 mL) intradermally.
Delegation Considerations
The skill of administering ID injections cannot be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). The nurse directs the NAP about:
▪ Potential medication side effects and reporting their occurrence to the nurse.
▪ Reporting any change in the patient’s condition to the nurse.
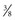 to
to  inch
inch


