Skill 13
Chest Tube Care
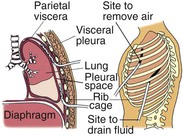
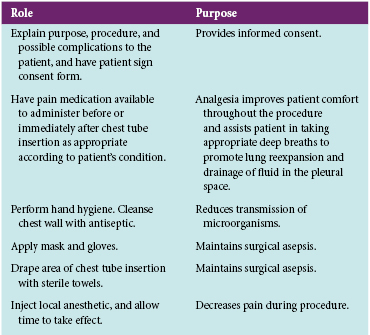
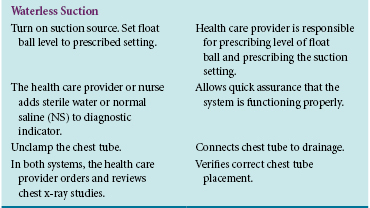
A chest tube is a large catheter inserted through the thorax to remove fluid (effusions), blood (hemothorax), and/or air (pneumothorax). The location of the chest tube indicates the type of drainage expected. Apical (second or third intercostal space) and anterior chest tube placement promotes removal of air. Chest tubes placed low (usually in the fifth or sixth intercostal space) and posterior or lateral drain fluid (Fig. 13-1). A mediastinal chest tube is placed in the mediastinum, just below the sternum (Fig. 13-2), and is connected to a drainage system. This tube drains blood or fluid, preventing its accumulation around the heart. This skill reviews the nursing responsibilities and interventions related to the safe management of chest tubes. Review the roles and responsibilities of the health care provider for chest tube placement (Table 13-1). There are two types of commercial drainage systems: the water-seal and the waterless systems.
Delegation Considerations
The skill of chest tube management cannot be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). The nurse directs the NAP about:
Equipment
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree