Skill 10
Blood Pressure by Auscultation
Upper Extremities, Lower Extremities, Palpation
The most common technique of measuring blood pressure is auscultation with a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope. As the sphygmomanometer cuff is deflated, the five different sounds heard over an artery are called Korotkoff phases. The sound in each phase has unique characteristics (Fig. 10-1). Blood pressure is recorded with the systolic reading (first Korotkoff sound) before the diastolic (beginning of the fifth Korotkoff sound). The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is the pulse pressure. For a blood pressure of 120/80, the pulse pressure is 40.
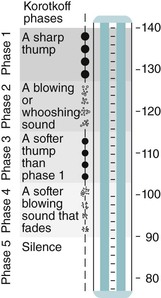
Fig. 10-1 The sounds auscultated during blood pressure (BP) measurement can be differentiated into five Korotkoff phases. In this example, the BP is 140/90 mm Hg.
Delegation Considerations
The skill of blood pressure measurement can be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP) unless the patient is considered unstable (e.g., hypotensive). The nurse instructs the NAP by: