Vascular Disorders
An aneurysm is a localized dilation of a blood vessel or cardiac chamber wall because of congenital or acquired weakness of the muscle. Because of the constant pressure it sustains, the aorta is particularly susceptible. The abdominal aorta is involved most of the time and the remaining incidence is attributable to the thoracic aorta. Peripheral arteries are less often affected. A popliteal artery aneurysm is third in order of frequency. Ventricular aneurysms may occur in the heart, and cerebral aneurysms occur in the brain. Aneurysms are potentially life threatening because rupture and hemorrhage or thromboembolism may occur.
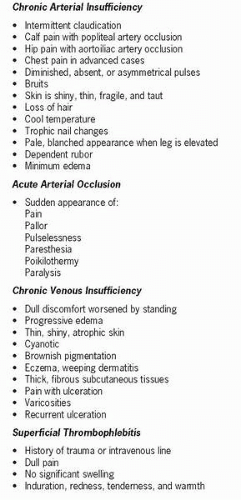
Chronic arterial occlusive disease is a slow progressive disorder in which partial or total arterial occlusion, predominantly in the lower extremities, deprives the extremities of oxygen and nutrients. The primary cause is atherosclerosis. Varicose veins or varicosities are distended, tortuous, palpable superficial veins of the lower extremity. Veins contain valves that prevent backflow and pooling of blood. Primary varicosities originate in the superficial saphenous veins that are dilated with or without incompetent valves. Chronic venous insufficiency is inadequate venous return over time.
TERMS
 Aneurysms are potentially life threatening because rupture and hemorrhage or thromboembolism may occur.
Aneurysms are potentially life threatening because rupture and hemorrhage or thromboembolism may occur.There are two major classifications of aneurysm: true aneurysms and false aneurysms or pseudoaneurysms. True aneurysms occur as a result of atrophy of the medial layer of the artery. The wall dilates but at least one wall of the artery remains intact. True aneurysms are further subdivided based on shape into a saccular aneurysm, a bulge with a narrow neck or spherical in shape connecting it to one side of the artery, and a fusiform aneurysm, circumferential and relatively uniformly shaped. Saccular aneurysms are associated with syphilis or congenital malformations. A false aneurysm involves the dissection of all the layers of the arterial wall and forms as a result of trauma, infection, or disruption of a suture line. This causes an extravascular hematoma or tamponade. Aortic dissection, sometimes referred to as dissecting aneurysm, occurs when a tear in the inner layer of an arterial wall allows blood to collect between layers of the wall. It is an acute, life-threatening condition requiring emergency surgery and has a high mortality rate.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree