Transdermal Drug Application
Through a measured dose of ointment or an adhesive patch applied to the skin, transdermal drugs deliver constant, controlled medication directly into the bloodstream for a prolonged systemic effect.
Nitroglycerin, one of the more common transdermal ointments, dilates coronary vessels for up to 4 hours.
Medications available as transdermal patches include scopolamine, used to treat motion sickness; estradiol, used for postmenopausal hormone replacement; clonidine, used to treat hypertension; nicotine, used for smoking cessation; and fentanyl, an opioid analgesic used to control chronic pain. Transdermal scopolamine can relieve motion sickness for as long as 72 hours, transdermal estradiol lasts for up to 1 week, transdermal clonidine and nicotine last for 24 hours, and transdermal fentanyl can last for up to 72 hours.
Contraindications for transdermal drug application include skin allergies or skin reactions to the drug. Transdermal drugs
shouldn’t be applied to broken or irritated skin, which would increase irritation, or to scarred or callused skin, which might impair absorption.
shouldn’t be applied to broken or irritated skin, which would increase irritation, or to scarred or callused skin, which might impair absorption.
Applying Nitroglycerin Ointment
Unlike most topical medications, nitroglycerin ointment is used for its transdermal systemic effect. It’s used to dilate the veins and arteries, improving cardiac perfusion in a patient with cardiac ischemia or angina pectoris.
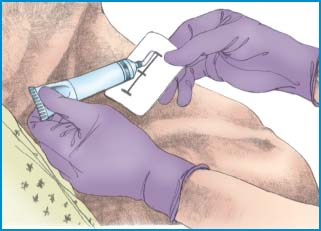
To apply nitroglycerin ointment, start by taking the patient’s baseline blood pressure so that you can compare it with later readings. Remove any previously applied nitroglycerin ointment. Gather your equipment. Nitroglycerin ointment, which is prescribed by the inch, comes with a rectangular piece of ruled paper to be used in applying the medication. Squeeze the prescribed amount of ointment onto the ruled paper (as shown below). Put on gloves, if desired, to avoid contact with the medication.
 |
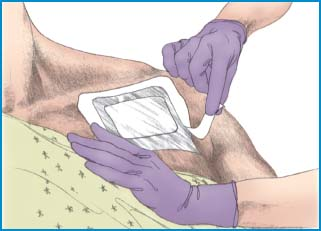
After measuring the correct amount of ointment, tape the paper—drug side down—directly to the skin (as shown below). (Some facilities require you to use the paper to apply the medication to the patient’s skin, usually on the chest or arm. Spread a thin layer of the ointment over a 3″ [7.6-cm] area.) For increased absorption, the doctor may request that you cover the site with a transparent semipermeable dressing.
 |
After 5 minutes, record the patient’s blood pressure. If it has dropped significantly and he has a headache (from vasodilation of blood vessels in his head), notify the doctor immediately; he may reduce the dose. If the patient’s blood pressure has dropped but he has no symptoms, instruct him to lie still until it returns to normal.
Equipment
Patient’s medication administration record and medical record ▪ gloves ▪ prescribed medication ▪ application strip or measuring paper (for nitroglycerin ointment) ▪ adhesive tape ▪ Optional: semipermeable dressing.
Implementation
Verify the doctor’s order order.1
Avoid distractions and interruptions when preparing and administering the medication to prevent medication errors.2
Compare the medication label to the order and verify that the medication is correct.3
Check the expiration date on the medication; don’t give the medication if it has expired.
Check the patient’s medical record for an allergy to the prescribed medication. If an allergy is present, don’t administer the medication; notify the doctor.

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
