Transcranial Doppler Monitoring
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography is a noninvasive method of monitoring blood flow in the intracranial vessels, specifically the circle of Willis. This procedure is used on the intensive care unit to monitor patients who have experienced cerebrovascular disorders, such as stroke, head trauma, or subarachnoid hemorrhage. It can help detect intracranial stenosis, vasospasm, and arteriovenous malformations as well as assess collateral pathways. Because it has the advantage of monitoring a continuous waveform, it can be used in intraoperative monitoring of cerebral circulation.
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography is also used to monitor the effect of intracranial pressure changes on the cerebral circulation, to monitor patient response to various medications, and to evaluate carbon dioxide reactivity, which may be impaired or lost from arterial obstruction or trauma. In addition, it has been used to confirm brain death.
The transcranial Doppler unit transmits pulses of high-frequency ultrasound, which are then reflected back to the transducer by the red blood cells moving in the vessel being monitored. This information is then processed by the instrument into an audible signal and a velocity waveform, which is displayed on the monitor. The displayed waveform is actually a moving graph of blood flow velocities with time displayed along the horizontal axis, velocity displayed along the vertical axis, and amplitude represented by various colors or intensities within the waveform. The heart’s contractions speed up the movement of blood cells during systole and slow it down during diastole, resulting in a waveform that varies in velocity over the cardiac cycle.
The major benefits of transcranial Doppler monitoring are that it provides instantaneous, real-time information about cerebral blood flow and that it’s noninvasive and painless for the patient. Also, the unit itself is portable and easy to use. The major disadvantage is that it relies on the ability of the ultrasound waves
to penetrate thin areas of the cranium; this is difficult if the patient has thickening of the temporal bone, which increases with age.
to penetrate thin areas of the cranium; this is difficult if the patient has thickening of the temporal bone, which increases with age.
The transcranial Doppler unit should always be used with its power set at the lowest level needed to provide an adequate waveform. This procedure requires specialized training to ensure accurate vessel identification and correct interpretation of the signals.
Equipment
Transcranial Doppler unit ▪ transducer with an attachment system ▪ terry cloth headband ▪ ultrasonic coupling gel ▪ marker.
Implementation
Verify the doctor’s order.
Confirm the patient’s identity using at least two patient identifiers according to your facility’s policy.4
Explain the procedure to the patient, and answer any questions he has about the procedure as thoroughly as possible.
Place the patient in the proper position, usually the supine position.
Turn the Doppler unit on and observe as it performs a self-test.
Enter information as prompted by the Doppler unit. Depending on the unit you’re using, you may need to enter the patient’s name, identification number, diagnosis, or the doctor’s name.
Indicate the vessel that you wish to monitor, usually the right or left middle cerebral artery. You’ll also need to set the approximate depth of the vessel within the skull (50 mm to 56 mm for the middle cerebral artery).
Increase the power level to 100% to initially locate the signal. You can later decrease the level as needed, depending on the thickness of the patient’s skull.
Examine the temporal region of the patient’s head, and mentally identify the three windows of the transtemporal access route: posterior, middle, and anterior (as shown below).
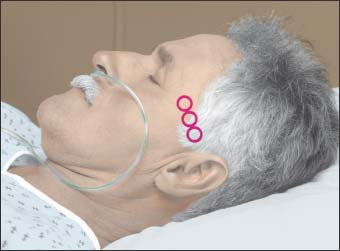
Apply a generous amount of ultrasonic gel at the level of the temporal bone between the tragus of the ear and the end of the eyebrow, over the area of the three windows.
Place the transducer on the posterior window. Angle the transducer slightly in an anterior direction, and slowly move it in a narrow circle. This movement is commonly called the flashlighting technique. As you hold the transducer at an angle and perform flashlighting, also begin to very slowly move the transducer forward across the temporal area. As you do this, listen for the audible signal with the highest pitch. This sound corresponds to the highest velocity signal, which corresponds to the signal of the vessel you are assessing. You can also use headphones to let you better evaluate the audible signal and provide patient privacy.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
