Swab Specimen Collection
Correct collection and handling of swab specimens helps laboratory staff members identify pathogens accurately with a minimum of contamination from normal bacterial flora.
Collection methods vary depending on the type of specimen being collected. For instance, collection of throat, nasopharyngeal, wound, external ear, and eye specimens usually involves sampling inflamed tissues and exudates, typically using sterile swabs of cotton or other absorbent material; wound exudate may also be aspirated into a syringe. Collection of fluid from the middle ear is performed by a doctor using a needle and syringe.
Because the normal bacterial flora in stool include several potentially pathogenic organisms, bacteriologic examinations are valuable for identifying pathogens that cause overt GI disease—such as typhoid and dysentery—and carrier states. A sensitivity test may follow isolation of the pathogen. Identifying the organism is vital to treat the patient, to prevent possible fatal complications (especially in a debilitated patient), and to prevent the spread of a severe infectious disease.
Equipment
Gloves ▪ penlight ▪ sterile swab (cotton wool or synthetic fiber) ▪ sterile culture tube with transport medium or commercial collection kit ▪ specimen label ▪ laboratory request form ▪ laboratory
biohazard transport bag ▪ Optional: mask and other personal protective equipment.
biohazard transport bag ▪ Optional: mask and other personal protective equipment.
Additional Equipment for Throat and Nasopharyngeal Specimen Collection
Tongue blade.
Additional Equipment for Wound Specimen Collection
Two pairs of sterile gloves ▪ chlorhexidine swabs ▪ sterile normal saline solution ▪ sterile 10-mL syringe ▪ sterile 21G needle ▪ anaerobic culture tube ▪ supplies to apply new dressing ▪ Optional: rubber stopper for needle.
Additional Equipment for Middle Ear Specimen Collection
Normal saline solution ▪ 2″ × 2″ gauze pads ▪ sterile 10-mL syringe and sterile 22G 1″ needle.
Additional Equipment for Eye Specimen Collection
Sterile normal saline solution ▪ two 2″ × 2″ gauze pads ▪ sterile wire culture loop (for corneal scraping).
Additional Equipment for Rectal Specimen Collection
Soap and water ▪ washcloth ▪ normal saline solution.
Implementation
Verify the doctor’s order.
Confirm the patient’s identity using at least two patient identifiers according to your facility’s policy.4
Explain the procedure to the patient to ease his anxiety and ensure cooperation.
Throat Specimen Collection
Tell the patient that he may gag during the swabbing but that the procedure will probably take less than 1 minute.
Instruct the patient to sit erect at the edge of the bed or in a chair, facing you.
Ask the patient to tilt back his head. Depress his tongue with the tongue blade, and illuminate his throat with the penlight to check for inflamed areas.5
If the patient starts to gag, withdraw the tongue blade and tell him to breathe deeply. Once he’s relaxed, reinsert the tongue blade but not as deeply as before. Encourage the patient to close his eyes or stare at the ceiling to promote cooperation.
Open and remove the swab, taking care not to touch the tip with your hands because the swab is sterile.6 If you touch the swab, discard it and obtain a new swab.
Using the swab, wipe the tonsillar areas from side to side, including any inflamed or purulent sites. Make sure you don’t touch the tongue, cheeks, saliva, or teeth with the swab to avoid contaminating it with oral bacteria.5
Move the swab into the posterior pharynx and wipe the area using a gentle side-to-side sweeping motion.
Withdraw the swab and immediately place it in the culture tube.5 If you’re using a commercial kit, crush the ampule of culture medium at the bottom of the tube, and then push the swab into the medium to keep the swab moist.
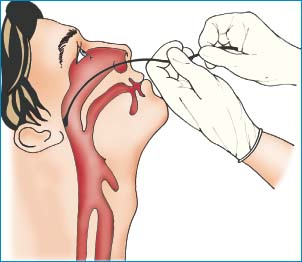
Nasopharyngeal Specimen Collection
Tell the patient that he may gag or feel the urge to sneeze during the swabbing but that the procedure takes less than 1 minute.
Have the patient sit erect at the edge of the bed or in a chair, facing you.
Ask the patient to blow his nose to clear his nasal passages. Then check his nostrils for patency with a penlight.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access