Micturition and Incontinence
Functional incontinence occurs in infants and young children when the bladder reaches a certain fullness. By the age of 2 or 3, a child learns to recognize the signals indicating the urge to void, and bladder training can begin. Enuresis, or bed-wetting, may last until late childhood. Children who sleep deeply may not notice the urge to void, and bed-wetting occurs. Elders with cognitive impairment may have functional incontinence.
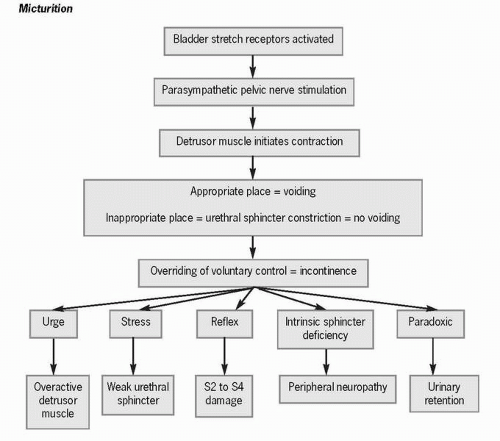 Figure 61-1 Micturition. |
As the bladder fills to between 150 and 300 cc, stretch receptors in the bladder walls are activated, creating the sensation of the need to void. Parasympathetic pelvic nerves transmit this signal to the detrusor muscle, initiating bladder contractions. The greater the amount of urine in the bladder, the stronger the impulse to micturate. Sympathetic nerve innervation of the detrusor muscle and internal sphincter prevents premature
parasympathetic stimulation and maintains the muscle tone of the internal sphincter. Higher-level motor impulses inhibit the voiding reflex by constricting the urethral sphincter and delaying voiding. Generally, ignoring the urge to void prevents release of the external sphincter, and neuron fatigue delays further stimulation of the voiding reflex arc for a few minutes to 1 hour. If the urge to void continues to be ignored, bladder reflex contractions eventually take over and cause involuntary voiding. Although micturition is generally under voluntary control, an overfilled or irritated bladder causes incontinence or the involuntary passage of urine.
parasympathetic stimulation and maintains the muscle tone of the internal sphincter. Higher-level motor impulses inhibit the voiding reflex by constricting the urethral sphincter and delaying voiding. Generally, ignoring the urge to void prevents release of the external sphincter, and neuron fatigue delays further stimulation of the voiding reflex arc for a few minutes to 1 hour. If the urge to void continues to be ignored, bladder reflex contractions eventually take over and cause involuntary voiding. Although micturition is generally under voluntary control, an overfilled or irritated bladder causes incontinence or the involuntary passage of urine.
 Although micturition is generally under voluntary control, an overfilled or irritated bladder causes incontinence.
Although micturition is generally under voluntary control, an overfilled or irritated bladder causes incontinence.The act of staying continent requires that a person have the motivation to do so, the ability to use toilet facilities, adequate mental functioning, and manual dexterity to manage clothing. Approximately 13 million adults over the age of 60 have either transient or chronic urinary incontinence. Complications of urinary incontinence include skin breakdown, depression, caregiver and personal stress, social isolation, and economic hardship caused by the cost of incontinence-related supplies. It is estimated that 50% of institutionalized elderly and 11% to 55% of community-dwelling elderly experience urinary incontinence. As a person ages, bladder capacity, sphincter tone, sensation, and the ability to inhibit detrusor contractions decrease, causing the involuntary passage of urine while the person is awake or, in some instances, asleep.
 Approximately 13 million adults over the age of 60 have either transient or chronic urinary incontinence.
Approximately 13 million adults over the age of 60 have either transient or chronic urinary incontinence. Complications of urinary incontinence include skin breakdown, depression, caregiver and personal stress, social isolation, and economic hardship.
Complications of urinary incontinence include skin breakdown, depression, caregiver and personal stress, social isolation, and economic hardship.Pathophysiology
Transient incontinence can be caused by many things, including delirium, infection, atrophic urethritis or vaginitis, medications, psychological factors, high urine output, restricted mobility, and fecal impaction.
Delirium prevents the patient from recognizing the urge to void and finding the nearest toilet. A symptomatic bladder infection leads to incontinence because the bladder and urethra are irritated. Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, alcohol, caffeine, and diuretics are the most common cause of transient incontinence. A severely depressed person may lack the motivation to stay continent. Nocturia and a high nighttime urine output may occur in patients with congestive heart failure as peripheral edema is mobilized once they assume a recumbent position. The reason fecal impaction causes urinary incontinence is not known; however, once the impaction has been corrected, continence generally resumes. Chronic incontinence occurs when the bladder loses its ability to store urine or empty urine effectively.
Delirium prevents the patient from recognizing the urge to void and finding the nearest toilet. A symptomatic bladder infection leads to incontinence because the bladder and urethra are irritated. Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, alcohol, caffeine, and diuretics are the most common cause of transient incontinence. A severely depressed person may lack the motivation to stay continent. Nocturia and a high nighttime urine output may occur in patients with congestive heart failure as peripheral edema is mobilized once they assume a recumbent position. The reason fecal impaction causes urinary incontinence is not known; however, once the impaction has been corrected, continence generally resumes. Chronic incontinence occurs when the bladder loses its ability to store urine or empty urine effectively.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


