Mechanical Traction Management
Mechanical traction exerts a pulling force on a part of the body— usually the spine, pelvis, or long bones of the arms and legs. It can be used to reduce fractures, treat dislocations, correct or prevent deformities, improve or correct contractures, or decrease muscle spasms. Depending on the injury or condition, an orthopedist may order either skin or skeletal traction.
Applied directly to the skin and thus indirectly to the bone, skin traction is ordered when a light, temporary, or noncontinuous pulling force is required. Contraindications for skin traction include a severe injury with open wounds, an allergy to tape or other skin traction equipment, circulatory disturbances, dermatitis, and varicose veins.
With skeletal traction, an orthopedist inserts a pin or wire through the bone and attaches the traction equipment to the pin or wire to exert a direct, constant, longitudinal pulling force. Indications for skeletal traction include fractures of the tibia, femur, and humerus. Infections such as osteomyelitis contraindicate skeletal traction.
The design of the patient’s bed usually dictates the type of traction frame used.
Setup of the specific traction can be done by a nurse with special skills, an orthopedic technician, or the doctor. Instructions for setting up these traction units usually accompany the equipment.
After the patient is placed in the specific type of traction ordered by the orthopedist, the nurse is responsible for assessing and managing the patient’s pain; preventing complications from immobility; routinely inspecting the equipment; adding traction weights, as ordered; and, in patients with skeletal traction, monitoring the pin insertion sites for signs of infection.
Equipment
IV-Type Basic Frame
102″ (259 cm) plain bar ▪ 27″ (69 cm) double-clamp bar ▪ 48″ (122 cm) swivel-clamp bar ▪ two 36″ (91 cm) plain bars ▪ four 4″ (10 cm) IV posts with clamps ▪ cross clamp ▪ trapeze with clamp ▪ wall bumper or roller.
IV-Type Balkan Traction Frame
Two 102″ plain bars ▪ two 27″ double-clamp bars ▪ two 48″ swivel-clamp bars ▪ five 36″ plain bars ▪ four 4″ IV posts with clamps ▪ eight cross clamps ▪ trapeze with clamp ▪ wall bumper or roller.
Claw-Type Basic Frame
102″ plain bar ▪ two 66″ (168 cm) swivel-clamp bars ▪ two upper-panel clamps ▪ two lower-panel clamps ▪ trapeze with clamp ▪ wall bumper or roller.
Preparation of Equipment
Arrange with central supply or the appropriate department to have the traction equipment transported to the patient’s room on a traction cart.
Implementation
Confirm the doctor’s order.
Confirm the patient’s identity using at least two patient identifiers according to your facility’s policy.1
Explain the purpose of traction to the patient and answer all questions to decrease anxiety and increase cooperation. Emphasize the importance of maintaining proper body alignment after the traction equipment is set up.
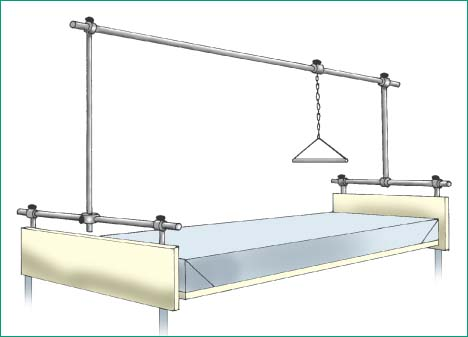
IV-Type Basic Frame
Attach one 4″ IV post with clamp to each end of both 36″ horizontal plain bars.
Secure an IV post in each IV holder at the bed corners. Using a cross clamp, fasten the 48″ vertical swivel-clamp bar to the middle of the horizontal plain bar at the foot of the bed.
Fasten the 27″ vertical double-clamp bar to the middle of the horizontal plain bar at the head of the bed.
Attach the 102″ horizontal plain bar to the tops of the two vertical bars, making sure the clamp knobs point up.
Using the appropriate clamp, attach the trapeze to the horizontal bar about 2′ (60 cm) from the head of the bed. (See IV-type basic traction frame.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access