Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
TERMS
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic (HHNK) syndrome
QUICK LOOK AT THE CHAPTER AHEAD
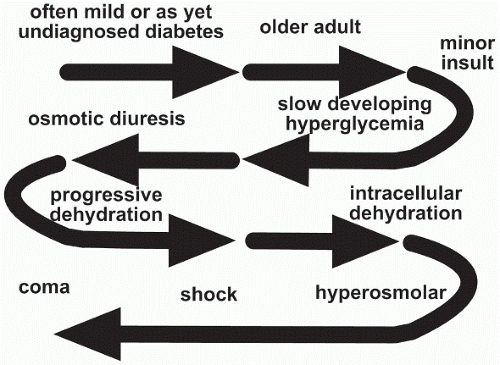
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic (HHNK) syndrome is a medical emergency that primarily affects patients with type 2 diabetes who can produce enough insulin to keep them from a state of acidosis but not enough to counteract the accumulation of excess glucose and the complicating high osmolarity and extracellular fluid loss. This syndrome is manifested by a blood sugar usually greater than 600 mg/dL and plasma osmolarity of 310 mOsm/L. In this chapter we review the causes and clinical manifestations of HHNK syndrome along with treatment and nursing implications.
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic (HHNK) syndrome is a complication of diabetes that primarily affects patients with type 2 diabetes. It is a medical emergency that affects individuals who can produce enough insulin to keep them from a state of acidosis but not enough to counteract the accumulation of excess glucose and the complicating high osmolarity and extracellular fluid loss. This event is frequently precipitated by a stressful event such as infection, trauma, myocardial infarction, thrombolytic events, or acute pancreatitis. It also has been associated with certain medications, such as phenytoin and thiazide diuretics, and procedures, such as peritoneal dialysis. Intravenous solutions containing a high glucose content, such as hyperalimentation
or enteral feedings, have also been documented as precipitating HHNK syndrome. Older patients with a history of type 2 diabetes present with HHNK syndrome along with a recent history of polyuria and inadequate fluid intake.
or enteral feedings, have also been documented as precipitating HHNK syndrome. Older patients with a history of type 2 diabetes present with HHNK syndrome along with a recent history of polyuria and inadequate fluid intake.
 HHNK syndrome primarily affects patients with type 2 diabetes and is frequently precipitated by a stressful event, certain medications, intravenous solutions, or enteral feedings.
HHNK syndrome primarily affects patients with type 2 diabetes and is frequently precipitated by a stressful event, certain medications, intravenous solutions, or enteral feedings.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Get Clinical Tree app for offline access