Craniotomy
This procedure involves creation of a surgical incision into the skull, thereby exposing the brain for treatment. These treatments may include ventricular shunting, excision of a tumor or abscess, hematoma aspiration, and aneurysm clipping.
Procedure
The surgical approach to a supratentorial craniotomy can be frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, or a combination of these areas. If structures below the tentorium are involved, the surgical approach to an infratentorial craniotomy utilizes an incision slightly above the neck in the back of the skull. In the operating room just before surgery, the anesthetist will start a peripheral I.V. line, a central venous pressure (CVP) line, and an arterial line. The CVP line provides access to remove air should an air embolus occur—a particular risk when posterior fossa surgery is performed in the sitting position.
After the patient receives a general or local anesthetic, the surgeon marks an incision line and cuts through the scalp to the cranium, forming a scalp flap that he folds to one side. He then bores four or five holes through the skull in the corners of the cranial incision and cuts out a bone flap. After pulling aside or removing the bone flap, he incises and retracts the dura, exposing the brain. (See Craniotomy: A window to the brain, page 220.)
The surgeon then proceeds with the surgery. Afterward, he reverses the incision procedure and covers the site with a sterile dressing.
Complications
Craniotomy has many potential complications, including infection, vasospasm, hemorrhage, air embolism, respiratory compromise, increased intracranial pressure (ICP), diabetes insipidus, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of diuretic hormone, seizures, and cranial nerve damage; the degree of risk depends largely on the patient’s condition and the surgery’s complexity.
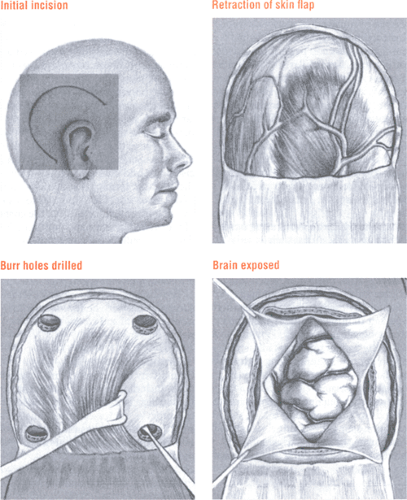
Craniotomy: A window to the brain
To perform a craniotomy, the surgeon incises the skin, clamps the aponeurotic layer, and retracts the skin flap. He then incises and retracts the muscle layer and scrapes the periosteum off the skull.
Next, using an air-driven or electric drill, he drills a series of burr holes in the corners of the skull incision. During drilling, warm saline solution is dripped into the burr holes, and the holes are suctioned to remove bone dust. Once drilling is complete, the surgeon uses a dural elevator to separate the dura from the bone around the margin of each burr hole. He then saws between the burr holes to create a bone flap. He either leaves this flap attached to the muscle and retracts it or detaches the flap completely and removes it. In either case, the flap is wrapped to keep it moist and protected.
Finally, the surgeon incises and retracts the dura, exposing the brain.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree