Bone Physiology
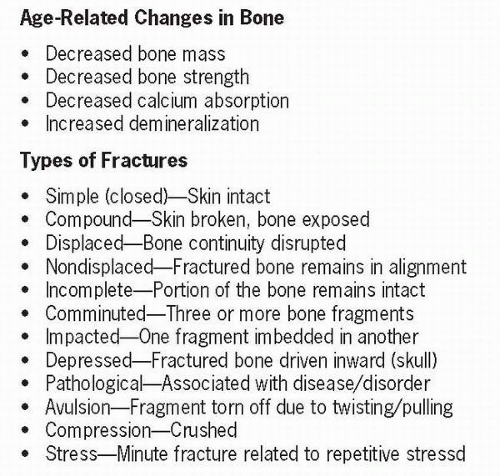
The human body is made up of 206 bones, which provide support and protection for soft tissue and body organs. Bones work interdependently with muscles and ligaments that allow for movement. There are four categories of bones, all of which provide specific functioning to the particular part of the body that makes up the framework. Any impairment of the bone due to disease or trauma affects its ability to properly function.
Table 65-1 Structural Elements of Bone | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The main function of bone is to protect and support internal organs of the body. Bones also function as an attachment site for muscles and skeletal tissue that allow for movement. Bone consists of an organic matrix upon which mineral salts are deposited. Protein, vitamin A, and vitamin C are needed for its formation by fibroblasts. Calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D are needed to form the inorganic compounds. Bone serves as a reservoir for calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals. Cancellous or trabecular bone is made up of thin plates, is spongy, and contains marrow. It is formed in response to stress and is found in bones
such as vertebrae and skull as well as the ends of long bones. The interlacing structure of these plates provides tensile strength and structural support for compact bone. Compact or cortical bone is found primarily in the long bones (upper and lower extremities) and in the outer layers of all bones. It is firm, dense, and resistant to compression and shearing.
such as vertebrae and skull as well as the ends of long bones. The interlacing structure of these plates provides tensile strength and structural support for compact bone. Compact or cortical bone is found primarily in the long bones (upper and lower extremities) and in the outer layers of all bones. It is firm, dense, and resistant to compression and shearing.
Collagen is the basic building block of bone matrix. It provides resilience or tensile strength. Without the collagen matrix, bone would be too hard and brittle. Calcium and other minerals lend strength and rigidity and provide compressive strength to bone. Ground substance consisting of protein polysaccharides or glycosaminoglycans serves as an adhesive between the layers of collagen matrix. It serves as a medium for diffusion of nutrients, oxygen, waste products, electrolytes, and minerals between bone tissue and blood vessels and influences calcium deposition and calcification. Vitamins A and C are also needed for its formation.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree