Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
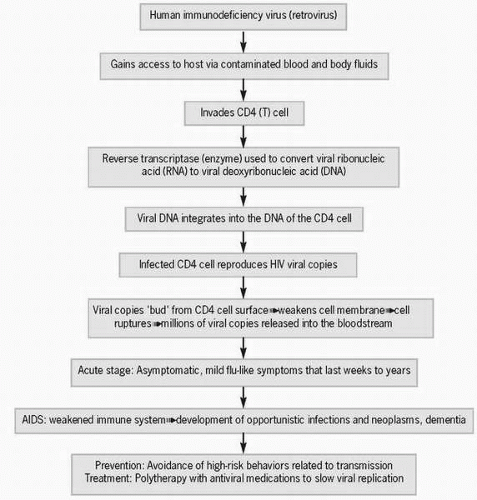
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a result of cell-mediated (T cell) immune system failure caused by the proliferation of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which replicates by invading T cells, thus weakening the immune system. Since it was first identified in 1981, HIV has reached pandemic proportions, currently infecting approximately 40 million people worldwide. HIV infection remains fatal, although both the quantity and quality of life have been vastly improved for people with the disease because of advances in pharmacotherapy.
HIV is the second leading cause of death in the 24- to 44-year age group in the United States. Approximately 950,000 people in the United States are HIV positive and approximately 415,000 have AIDS. Women account for approximately 27% of new AIDS cases, up from 7% in 1985. African-Americans have the highest rate of new AIDS cases compared with other ethnic groups.
 Since it was first identified in 1981, HIV has reached pandemic proportions, currently infecting approximately 40 million people worldwide.
Since it was first identified in 1981, HIV has reached pandemic proportions, currently infecting approximately 40 million people worldwide. Women account for approximately 27% of new AIDS cases, up from 7% in 1985.
Women account for approximately 27% of new AIDS cases, up from 7% in 1985.HIV is transmitted through direct contact with infected blood, blood products, and body fluids, including breast milk, vaginal/cervical secretions, and semen. It is also found in the cerebrospinal fluid and saliva of infected individuals. Two major types of the virus account for the majority of HIV infection: HIV-1 is found in most areas of the world and HIV-2 is found primarily in West African nations.
 HIV is transmitted through direct contact with infected blood, blood products, and body fluids, including breast milk, vaginal/cervical secretions, and semen.
HIV is transmitted through direct contact with infected blood, blood products, and body fluids, including breast milk, vaginal/cervical secretions, and semen.The risk of acquiring HIV from a needlestick injury is approximately 1:300. The risk of HIV transmission increases if the needlestick injury is deep, occurs with a hollow-bore needle, if there was visible blood on the needle before the injury, and if the infected person was in an advanced stage of the disease. By contrast, estimated HIV infection rates from sharing needles with an HIV-infected individual are 1:150.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree